Auditorias De Sistemas Fotovoltaicos: The Key to Unlocking Solar Performance and Financial Returns
Auditorias De Sistemas Fotovoltaicos: The Key to Unlocking Solar Performance and Financial Returns
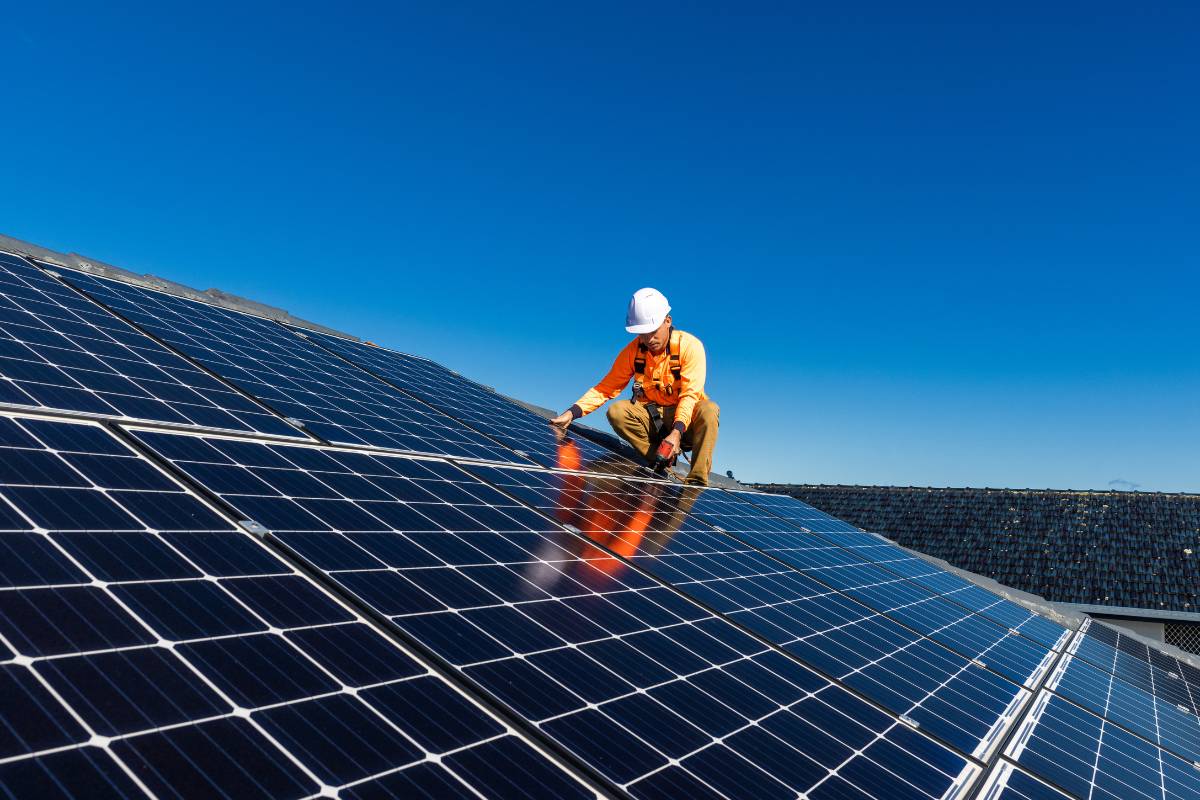
In an era defined by energy transition and climate urgency, Auditorias De Sistemas Fotovoltaicos—systematic evaluations of photovoltaic installations—have emerged as essential tools for homeowners, businesses, and utilities. These rigorous assessments go beyond surface checks, diving into technical performance, safety compliance, degradation trends, and economic viability. By transforming raw solar data into actionable insights, such audits ensure solar investments deliver maximum output, longevity, and return on investment.
As distributed solar adoption accelerates globally, understanding the depth and importance of these audits is no longer optional—it’s a strategic necessity.
The Core Objectives of Photovoltaic System Audits
Auditorias De Sistemas Fotovoltaicos serve multiple critical functions, each instrumental in maintaining optimal system operation. At their foundation, these audits verify: - **Energy Yield Accuracy**: Measuring actual electricity generation against expected performance based on irradiance, temperature, and panel efficiency.Discrepancies often reveal issues like soiling, shading, or inverter inflexibility. - **Component Health Assessment**: Detailed inspection of solar panels, inverters, combiners, and cabling to detect early signs of wear, microcracks, or electrical faults. Timely detection prevents cascading failures and costly downtime.
- **Compliance with Standards**: Ensuring installations meet national and international codes—such as IEC 61215 for module performance and NBR 16100 in Brazil or UL 1703 in the U.S.—providing legal and insurance protection. - **Financial Viability Analysis**: Evaluating return on investment by comparing energy production, savings, maintenance costs, and potential incentives against initial capital expenditure. “An audit isn’t just about checking boxes—it’s about seeing the invisible inefficiencies that quietly drain performance,” explains Dr.
Luís Ferreira, a renewable energy auditor and professor at the Federal University of São Paulo. “Without systematic validation, even newly installed systems can underperform by 20% or more.”
By combining on-site diagnostics with advanced monitoring software, auditors generate comprehensive reports translating complex data into reliable insights. This enables stakeholders—from facility managers to investors—to make informed decisions about maintenance, upgrades, or reinvestment.
Key Components Evaluated in a Photovoltaic System Audit A thorough Auditoria De Sistemas Fotovoltaicos leaves no critical element untested.
The following components form the audit’s backbone: - **Solar Panels**: Visual and electrical inspection for physical damage, discoloration, or power degradation. Devices measure SPDT (Single-Point Distribution Test Points) to assess panel-to-panel consistency. - **Inverters**: Prime candidates for failure due to heat stress or software obsolescence.
Audits include thermographic scans and firmware validation to ensure peak energy conversion. - **Mounting Structures**: Structural integrity checks identify corrosion, loosening, or improper angle alignment that can reduce efficiency and risk during storms. - **Electrical Connections**: Continuity, insulation resistance, and grounding fault tests prevent hazards like arc faults and electrical shocks.
- **Monitoring Infrastructure**: Integration of real-time data platforms enables predictive maintenance, allowing anomalies to be flagged before system-wide impacts occur.
Technology lies at the heart of modern audits. High-resolution thermal imaging detects “hotspots” in panels, indicating delamination or cell failure, while drones equipped with multispectral sensors now survey large solar farms with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
The Evolving Landscape of Auditing Standards and Best Practices Global solar deployment has spurred the development of rigorous auditing frameworks tailored to local climates, regulations, and technology.
In Europe, ISO/IEC 17020 certifications guide auditors through standardized, repeatable testing. Meanwhile, North America increasingly adopts IEEE 1547 and UL 1741 standards to ensure grid interconnection safety. In emerging markets like India and Southeast Asia, audits incorporate island/accuracy metrics under variable irradiance conditions, reflecting region-specific challenges.
“Each system tells a unique story—climate exposure, installation quality, and aging patterns vary widely,” says Sofia Montenegro, a lead auditor with Sustainable Solar Solutions in Rio de Janeiro. “An effective audit adapts to these variables, delivering insights that generic checklists can’t capture.” Moreover, traceability and documentation have become non-negotiable. Auditors now employ blockchain-enabled logs and standardized digital report templates to ensure compliance transparency for regulators, financiers, and insurers.
Automation and artificial intelligence are transforming traditional audits. Machine learning models analyze years of performance data to predict degradation curves and spotlight underperforming strings before failures occur. This shift from reactive to proactive maintenance dramatically extends system lifespans and minimizes risk.
Economic and Regulatory Drivers Behind Mandatory Audits
Governments and utilities increasingly mandate regular audits to uphold grid reliability and investor confidence.In Brazil, Linac (private regulatory authority) now requires annual audits for commercial solar systems over 50 kW, reinforcing accountability. Similarly, the European Union’s Clean Energy Package promotes mandatory performance certifications linked to renewable energy subsidies, aligning audit rigor with policy incentives. Beyond compliance, these audits protect return on investment.
A 2023 study by the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) found that solar projects undergoing annual audits achieve 8–12% higher annual returns through optimized operations and reduced unplanned downtime. “Audits turn preventive maintenance into a competitive advantage,” notes Rafael Costa, director of operations at GreenVolt Energia. “They validate performance guarantees, support asset underwriting, and demonstrate due diligence—critical when securing loans or insurance.”
For investors and installers alike, audits are not optional legitimacy markers but operational imperatives.
They transform energy data into trusted capital intelligence, ensuring every watt generated translates into measurable value.
The Future of Photovoltaic Auditing: Toward Smarter, Integrated Systems As photovoltaic systems grow in scale and complexity—with hybrid storage, DIY solar kits, and grid-interactive installations on the rise—the demand for adaptive, data-rich auditing grows. Future audits will likely integrate real-time digital twins, where virtual replicas of installations simulate performance under changing conditions and recommend corrective actions autonomously. Smart sensors and IoT-enabled devices promise continuous remote monitoring, reducing visit frequency while enhancing audit frequency and precision.
Meanwhile, standardized open-source audit platforms encourage interoperability, allowing data to flow seamlessly between monitoring systems, finance software, and grid operators. “This is the next frontier,” says Dr. Ana Rocha, a renewable systems engineer at the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA).
“Auditing will evolve beyond checking systems to actively optimizing them—bridging technical performance with economic strategy.”
In an age where solar energy powers entire communities and industries, Auditorias De Sistemas Fotovoltaicos stand as silent guardians of efficiency, safety, and value. They transform raw sunlight into measurable returns, ensuring that every installation fulfills its promise—not just today, but for decades to come.




Related Post

Alan Walker’s 'Alone' Meets Incredibox: A Fusion of Emotional Depth and Chaotic Creativity
Pioneering Analysis of Ev.01: Unveiling Architecture Dynamics
Bhop Unblocked: Breaking Barriers to Access Premium Content with Freedom and Speed
Costa Mesa Police Internal Review Unveils Shocking Patterns in Use-of-Force Protocols and Accountability Gaps

