Bliss OS Live USB Won’t Boot? Try These Proven Fixes to Get Your Live System Running Again
Bliss OS Live USB Won’t Boot? Try These Proven Fixes to Get Your Live System Running Again
When Bliss OS Live USB refuses to boot after a failed attempt to run it on a device, users often face frustration—especially after investing time preparing the live environment for interviews, research, or quick offline computing. The Linux-based Bliss OS, designed for privacy, simplicity, and uninterrupted access to essential tools, suddenly becomes inaccessible, turning a useful tool into a lockbox. But boot issues are rarely irreversible.
With systematic troubleshooting, users can diagnose and resolve common failure points that prevent the live OS from launching. This guide explores the most effective fixes to restore functionality and ensure Bliss OS Live USB delivers on its promise of reliable, portable Linux performance.
At the heart of boot failures often lies a mismatch between hardware compatibility, corrupted partition tables, or system configuration errors.
Unlike full OS installations, live USBs rely on a single executable (typically `systemd-run` or a preferred init system) to initialize the system, making every component—from bootloader placement to partition integrity—critically important. Understanding these foundational elements enables targeted recovery without overcomplicating the process.
Check Bootloader Configuration and EFI Support
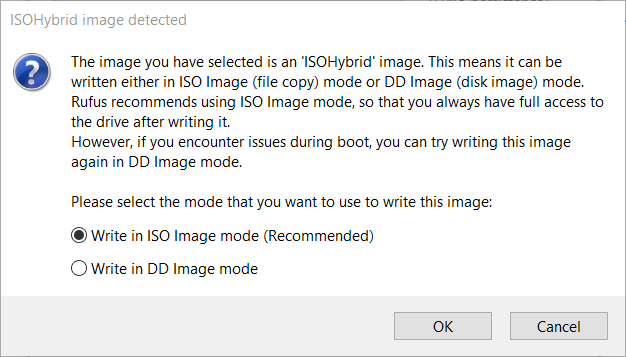
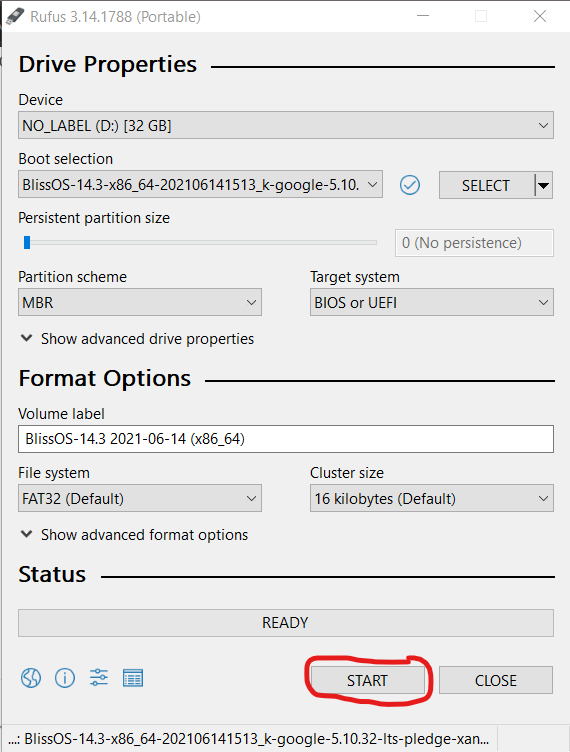
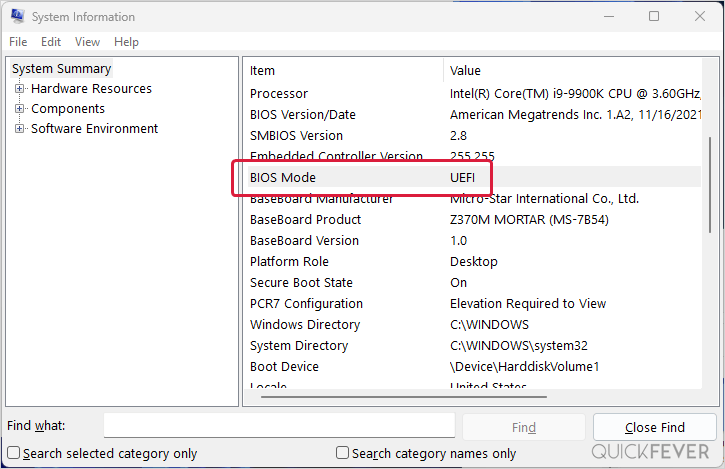
One of the most frequent causes of failure is an incompatible or misconfigured bootloader. Bliss OS Live USB uses the EFI (Extensible Firmware Interface) standard on modern systems, requiring both a valid EFI partition and a properly registered bootloader.If the USB fails to locate `efi/boot/loader` or the partition lacks the required `EFI` table, the system cannot initiate, often triggering a cold boot error or timeout. To verify bootloader readiness: - Confirm that the USB drive is formatted as FAT32 (Microsoft recommendations) with FAT32’s boot support intact—NTFS fails consistently with EFI boot. - Use `磁盘工具` (Disk Utility) or command-line tools like `efibootmgr` (on compatible hardware) to inspect the EFI boot entries.
- On UEFI systems, check BIOS/UEFI settings to ensure boot order prioritizes USB, or disable boot from removable media if present. “Many users skip verifying `efibootmgr`-based entries,” notes Linux system administrator Maria Lopez. “A missing or corrupted EFI boot entry often masquerades as a ‘ghost’ issue, but it’s usually a straightforward fix.”
If the EFI partition exists but the OS fails to start post-bootloader, the problem likely lies in the init process—either a missing system user, corrupt user cache, or a misconfigured systemd service.
Bliss OS uses lightweight systemd by default, so ensuring minimal but functional user environments prevents early crashes.
Troubleshoot Filesystem and Partition Integrity
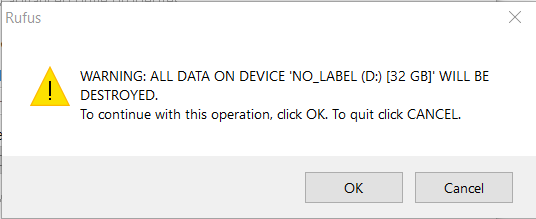
File system inconsistencies or corrupted partitions are silent killers of live USB usability. Even a seemingly healthy USB drive may suffer from bad sectors, improper formatting, or schema mismatches that prevent bootloaders from reading the root filesystem. Bliss OS depends on a well-structured ext4 or FAT32 roots partition; errors here halt execution before anything graphical loads.Essential steps include: - Booting from another OS (e.g., Ubuntu Live) to inspect the USB via Windows Recovery (using `bootrec /fixmbr` or `bootrec /fixboot`) and validate file system health. - Mounting the USB in Linux to `/mnt/bliss` with `mount -t ext4 /dev/sdXn /mnt/bliss` and running `fsck.ext4` to detect and repair file system anomalies. - Avoiding NTFS or exFAT unless absolutely necessary—these formats lack reliable EFI boot support and risk drive instability.
“Filesystem corruption is often subtle,” advises technician James Reed. “A quick `fsck` run can resolve invisible errors before they block the system—don’t assume ‘it just worked yesterday.’”
Users experiencing persistent timeouts or kernel panics should check kernel image versions. Bliss OS Live USB employs a curated kernel tailored for live environments; using an outdated or mismatched kernel may trigger boottime hangs, even if partitions are intact.
Verify USB Drive Health and Human Error
Hardware degradation or improper use often undermines the boot process.USB sticks endure mechanical wear, and repeated unnecessary ejections can damage firmware controllers. Even write-protection settings—whether enabled accidentally or via BIOS—can block device initialization. Recommended actions: - Test the drive on multiple hosts to rule out hardware failure.
Use tools like CrystalDiskInfo to check SMART status and detect impending drive failure. - Unmount the USB via Disk
Related Post
Jennelle Eliana Biography Age Wiki Net worth Bio Height Boyfriend
Decoding June 6 Zodiac Traits: The Key to Compatibility, Chemistry, and Cosmic Connections

