Decoding Plant Growth: Mastering Ap Biology Plant Hormones Through Effective Learning with Pogil Answers
Decoding Plant Growth: Mastering Ap Biology Plant Hormones Through Effective Learning with Pogil Answers
Plant hormones are the silent architects of growth, orchestrating everything from seed germination to flowering and senescence. Understanding their roles—beyond textbook diagrams—requires active engagement with core biological concepts, a task elegantly supported by the Pogil (Project Exploration Investigating Science) collaborative learning approach. This article explores key plant hormones through AP Biology content, leveraging Pogil-style inquiry to clarify how auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid, and ethylene coordinate complex developmental programs.
By examining real applications and forming hypothesis-driven connections, students gain a deep, intuitive grasp of hormonal regulation, turning abstract science into tangible understanding.
At the heart of plant development lies a dynamic hormonal network that ensures survival and reproduction in ever-changing environments. Each hormone serves a distinct function, yet their interactions form a delicate balance essential for coordinated growth. The Pogil framework enables learners to dissect these mechanisms through structured inquiry: questioning how hormones influence cell elongation, root formation, and stress responses.
Rather than passive memorization, students develop critical thinking by analyzing real data, predicting outcomes, and evaluating hormone-induced phenotypes.
Key Plant Hormones and Their Functional Roles
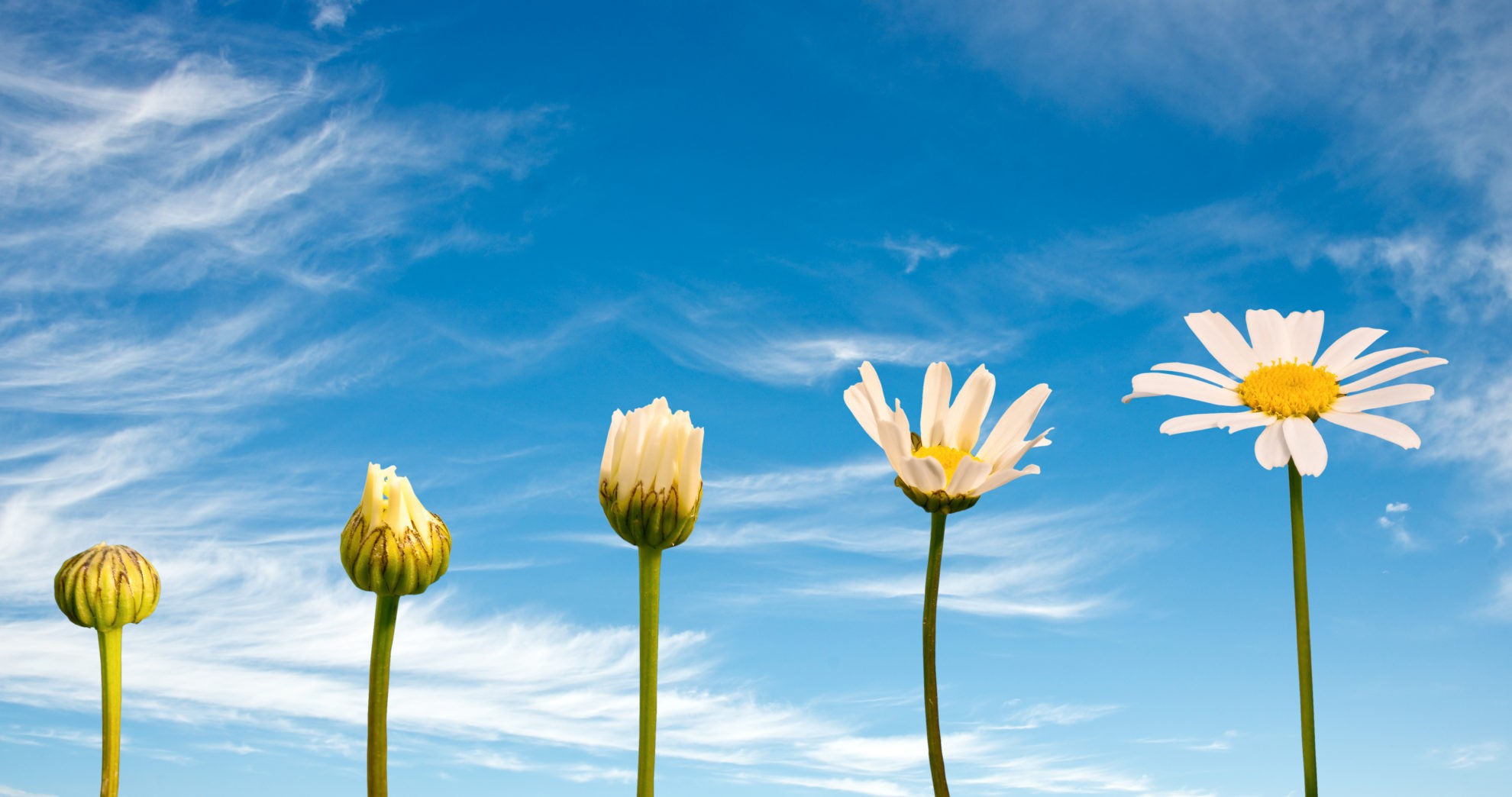
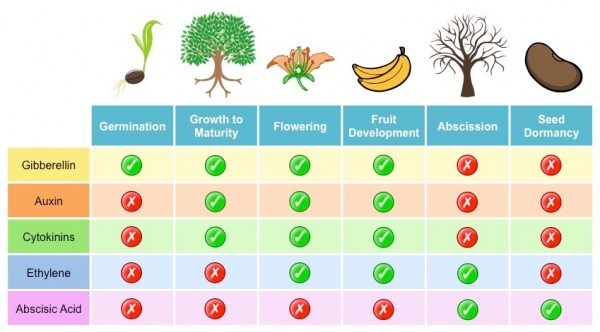
HS:Hormone | Primary Function | Pogil Insight --- | --- | --- Auxin | Stimulates cell elongation, apical dominance, phototropism | Students investigate auxin’s polar transport by modeling directional growth responders; activating PIN protein dynamics under light gradients. Gibberellins | Promote stem elongation, seed germination, and flowering | Learners analyze gibberellin’s role in breaking seed dormancy, linking hormone synthesis to ENT1-GID1 receptor activation and DELLA protein degradation. Cytokinins | Stimulate cell division, delay senescence, and regulate shoot development | Pogil activities highlight cytokinin-cytokinin balance via experiments on shoot bud outgrowth, showing how hormone ratios dictate tissue differentiation.Abscisic Acid (ABA) | Mediates stress responses, maintains dormancy, promotes stomatal closure | Through gut-level analysis of drought-induced gene expression, students uncover ABA’s protective signaling cascade that prepares plants for environmental challenge. Ethylene | Regulates fruit ripening, leaf abscission, and stress responses | Inquiry labs simulate ethylene biosynthesis inhibition, demonstrating how hormone levels modulate timing of ripe fruit development and premature leaf drop.
These hormones operate within an interconnected signaling network, where each influences others—golden rules unraveled through collaborative problem-solving in Pogil exercises.
For example, auxin and cytokinin ratios steer polarity and division planes, whereas gibberellins override dormancy signals only when ABA levels decline, illustrating hormonal antagonism central to plant adaptability.
Active Learning Through Pogil Activities: Building Mastery
Pogil’s student-centered approach transforms plant hormone study from abstract memorization into inquiry-driven discovery. The process typically unfolds in structured steps:
- Explore: Students engage with simple diagrams and excerpts, identifying hormone actions through visual and written cues.
- Explain: Working in small groups, learners articulate mechanisms—using precise terms like “gibberellin binding to receptor」と “DELLA protein stability”—to represent molecular events.
- Apply: Hands-on labs simulate hormone treatments in controlled environments, measuring germination rates, growth direction, or enzyme activity as tangible proof of hormonal impact.
- Evaluate: Guided reflection queries prompt analysis of why certain responses occur under specific conditions, reinforcing systems thinking.
One foundational Pogil scenario tasks students with diagnosing a stunted phenotype: “Root growth is impaired in young seedlings under high light and drought.” Learners hypothesize that elevated ABA triggered stomatal closure, reducing water uptake and auxin transport—eliciting measurable changes in turgor pressure and root tip elongation. Such investigations make causal relationships explicit, turning perception into scientific understanding.
Real-World Implications and Biological Significance
Plant hormones are not merely internal regulators but critical mediators of survival strategies.
Auxin gradients guide tropic responses enabling plants to seek light, while gibberellins unlock seed viability in seasonal environments. Cytokinins delay aging, ensuring sustained photosynthesis, whereas ethylene triggers rapid leaf drop to conserve energy during brisk autumn transitions. ABA, often termed the “stress hormone,” stands at the forefront of drought resilience, linking hormonal signaling to agricultural sustainability.
The Pogil approach emphasizes these real-world contexts, helping students see plant biology not as static facts but as a dynamic system vital to ecosystem health and food security.
For AP Biology students, mastering plant hormones via Pogil-style inquiry builds more than recall—it develops the ability to analyze hormonal networks, predict phenotypic outcomes, and appreciate biological complexity. As learning shifts from passive absorption to active construction, hormone-driven processes emerge with clarity: not as isolated signals, but as corners of a responsive, interconnected organismal symphony.
In essence, the intersection of plant hormone science and collaborative learning through structured exploration defines a powerful model for modern biology education. The Pogil methodology empowers students to decipher hormonal logic, transforming enigmatic biochemical pathways into intuitive, evidence-based understanding.
With each lesson, the invisible workings of auxins, gibberellins, and others come into focus—revealing nature’s elegant regulatory design behind the plant kingdom’s resilience.



Related Post
Dawn Hasbrouck Fox 32 Bio Wiki Age Twin Husband Salary and Net Worth
Berkeley Inmate Claims Innocence: Hidden Evidence Could Expose a Systemic Failure in Justice
Outback Opal Hunters Female Cast Now: Women Reigning Under the Southern Skies
Lucernating Access: How Globus Log In Powers Seamless Research Collaboration

