East Meets Central: The Dynamic Shift Across Time Zones from Eastern to Central Standard Time
East Meets Central: The Dynamic Shift Across Time Zones from Eastern to Central Standard Time
The seamless transition from Eastern Time to Central Time unfolds as a critical yet often unnoticed rhythm in North American life—bridging a nearly two-hour continental gap with precision, efficiency, and a degree of geographic necessity. This daily time shift, operating primarily across the U.S. Midwest and parts of Canada, reflects more than just clock changes; it shapes business schedules, travel planning, broadcasting, and digital communication.
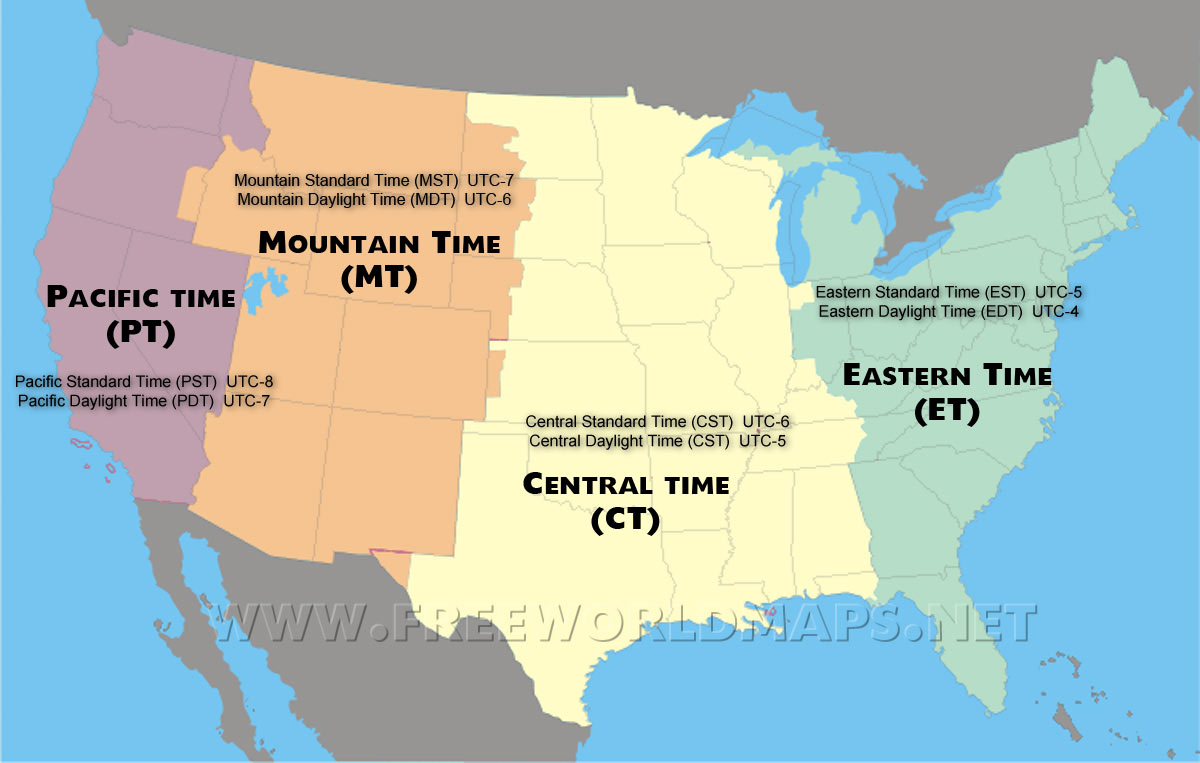
The temporal gap between Eastern Time (ET), centered on the Atlantic seaboard, and Central Time (CT), spanning the heartland from Chicago to Houston, creates a structured flow of operations that demands awareness and adaptation. Understand this bridge to navigate modern cross-continent life with confidence.
The Geography and Reality of the Eastern-to-Central Time Shift
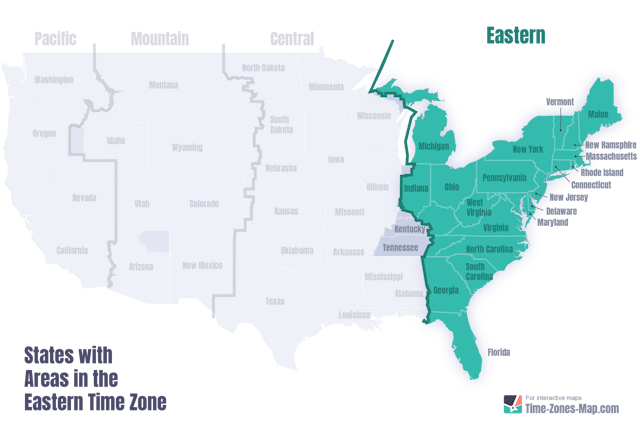
The Eastern Time Zone stretches from the Atlantic Coast—Boston, New York, and Miami—through dense urban corridors, ending just south of the Canadian border in parts of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia.In contrast, Central Time spans the expansive interior, anchored by Chicago and Oklahoma City, extending westward into the Rocky Mountain regions. The shift spans approximately two hours, varying slightly with daylight saving time shifts, which are synchronized across both zones. This two-hour offset isn’t arbitrary; it reflects historical, industrial, and geographic considerations.
Midwestern rail systems, 20th-century industrial work patterns, and broadcasting schedules evolved around this division, reinforcing its functional role. For professionals in finance, logistics, or media, recognizing the exact transition window—standard time and DST changes—is essential to avoid scheduling conflicts or operational delays.
To understand the shift’s mechanics, consider the time difference grid: when it’s 9:00 AM Eastern, Central Time is 7:00 AM; when Eastern peaks at 5:00 PM, Central matches at 3:00 PM.
This staggered start preserves overlap hours—typically 3:30 AM to 3:15 PM CT, aligning with midday in Eastern Time. This overlap supports crucial coordination points during the shift, especially in sectors like air traffic control, sports broadcasting, and corporate meetings. The misalignment reveals not only time zones but competing priorities: coastal financial centers versus inland manufacturing hubs, or northern schools ending the day earlier than those to the south.
Operational Impacts: Scheduling Across Two Time Zones
From an operational standpoint, the Eastern-to-Central transition influences millions daily.For example, Chicago metro businesses—home to major exchanges like the CME and pressing headquarters—must adjust internal timelines when coordinating with Atlanta, Dallas, or Minneapolis. A morning board meeting at 10:00 Eastern risks confusion if participants in Cincinnati or St. Louis are still in pre-breakfast hours.
“Clock crossings are real-time coordination challenges,” notes Dr. Lena Markov, time logistics expert at the International Time Consortium. “Teams must pre-verify timestamps, especially when synchronizing real-time data feeds or live broadcasts.” Transportation networks exemplify the shift’s reach.
Amtrak trains, freight rail dispatch, and regional airlines calibrate departure and arrival timelines across zones. A train scheduled to leave Chicago at 8:00 Eastern morning may depart St. Louis at 6:00 Central—accurate alignment prevents delays and ensures crew shifts align with operational zones.
Similarly, cargo logistics depend on precise time transfer points to synchronize warehouse operations: a shipment arriving in Indianapolis at 7:00 CT must be received by Chicago’s distribution center before 7:00 AM ET to meet 9:00 AM scheduling deadlines.
The Human Experience: Daily Adjustments and Cultural Nuances
Beyond logistics, the Eastern-to-Central shift shapes individual routines. For educators, the transition means students switch from 8:00 Eastern–3:00 CT core classes into a later school day, a change requiring strict time management and often affecting after-school plans.Parents balancing commutes face staggered start times and childcare transitions—few hours later east of Midwestern suburbs. Business travelers planning conferences must account for the time gap to avoid missed appointments or mental fatigue from abrupt temporal changes. Culturally, the shift underscores regional identities.
In cities like Detroit or Minneapolis, time awareness aligns with local work rhythms and weather patterns; in Gulf Coast towns like New Orleans, the shift blends with distinct social schedules. This duality—geographic mapping and cultural rhythm—makes the transition more than a technical detail; it’s a lived experience woven into daily life.
Technology now mediates much of the shift’s complexity.
Voice assistants recalend reminders, calendar apps auto-adjust time zones, and global communication platforms flag shifting windows. Yet human judgment remains vital. Missed transitions—like an unadjusted clock or a forgotten DST change—can cascade into missed calls, delayed shipments, or misaligned meetings.
Proactive awareness ensures continuity across the time divide, preserving both productivity and clarity.
Daylight Saving Time: A Beta-Powered Transitional Layer
The shifting of Central Time from standard to daylight saving—typically the second Sunday in March—adds a biannual pivot that amplifies precision needs. From March to November, Central Time drifts forward one hour from 2:00 AM local (standard time) to 3:00 AM (Daylight Time). This reset advances the full East-Central gap, making midday in Chicago two hours later than standard-time Chicago but only one hour ahead of CT during spring.Media and digital platforms now widely promote alerts—Apple’s clocks, Smartwatch sync, and enterprise software updates—highlighting the shift’s growing emphasis on universal time awareness. As the 2025 transition approaches, millions prepare for the recurring biannual rhythm, reinforcing its role in synchronized life.
The Eastern-to-Central Shift as a Backbone of Continental Connectivity
The interplay between Eastern and Central Time zones is far more than a geographic footnote—it’s a fundamental enabler of North America’s operational infrastructure.From finance floors to classroom halls, from freight yards to Friday evening sports broadcasts, the two-hour transition orderly sands the journey across a continent. As modern life grows ever interdependent, mastery of these time boundaries ensures accuracy, efficiency, and mutual understanding across regions. In understanding the flow from Eastern to Central, one gains not just time awareness, but a deeper appreciation for how human systems adapt to the Earth’s rotation—continuously, systematically, and with quiet precision.
This bridge over two hours powers progress, one synchronized minute at a time.
Related Post

Prisma Cloud & NIST 800-53: Orchestrating Cloud Security with Precision and Compliance

Revolutionizing Urban Mobility: HudsonNews Examines Smart Transit Systems Reshaping City Life
Skylar Blue Leak Exclusive: Unveiling Unbelievable Truths That Shock the World
Jeff Hardy Undergoes Eye Surgery During AEW Hiatus

