Harnessing Docker-Native VPCs: A Raspberry Pi Guide to Building and Managing Satellite Remote IoT Networks on Remoteiot Free
Harnessing Docker-Native VPCs: A Raspberry Pi Guide to Building and Managing Satellite Remote IoT Networks on Remoteiot Free
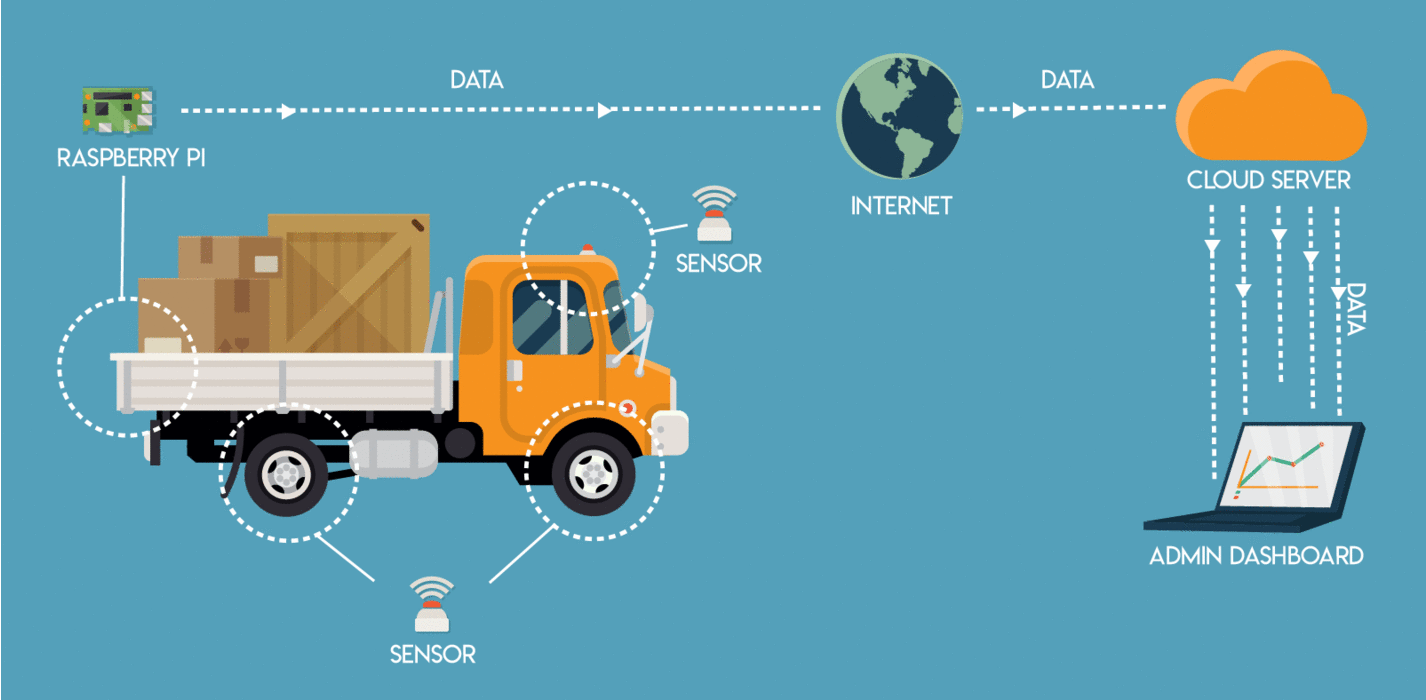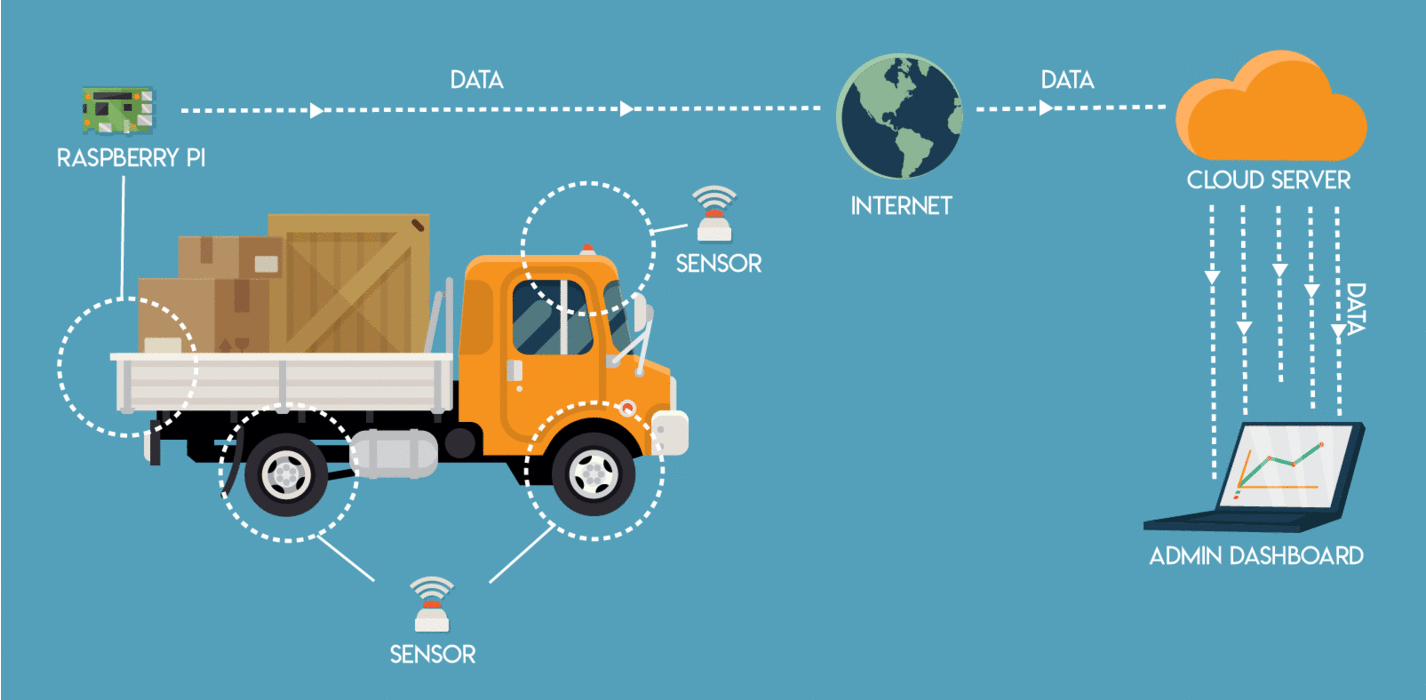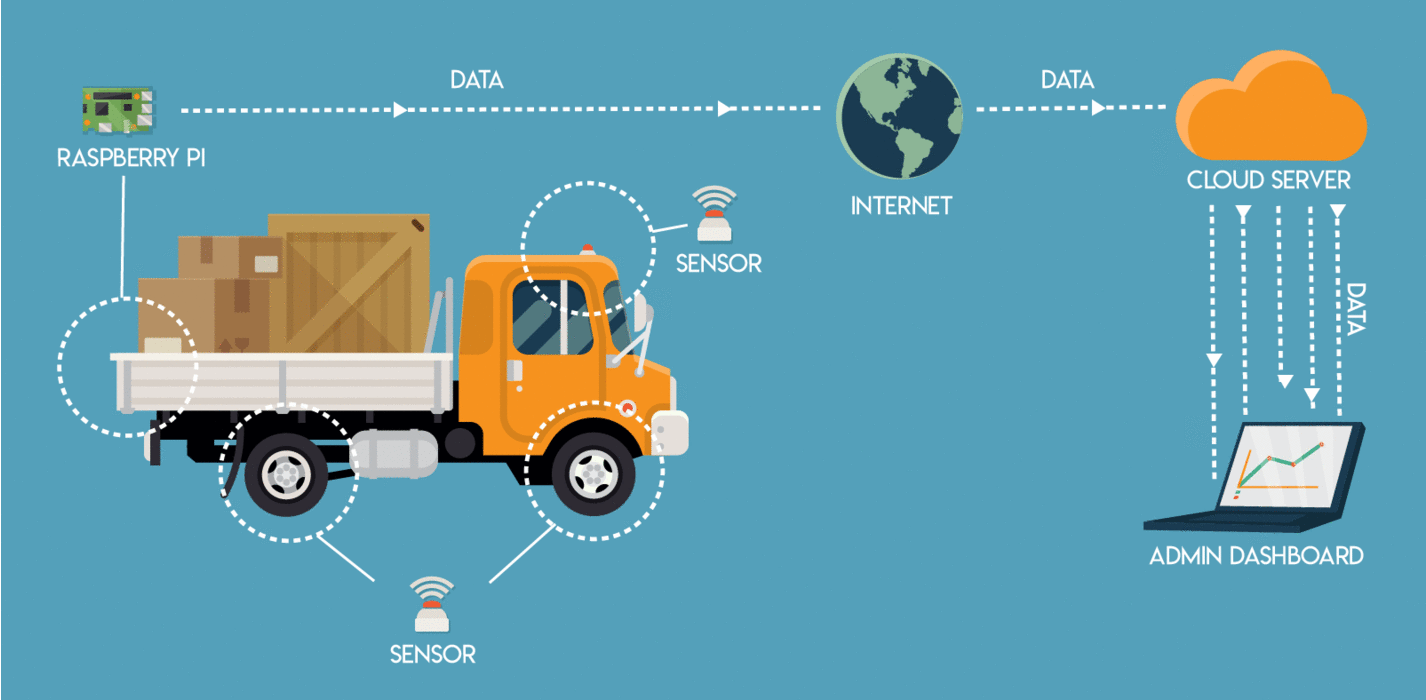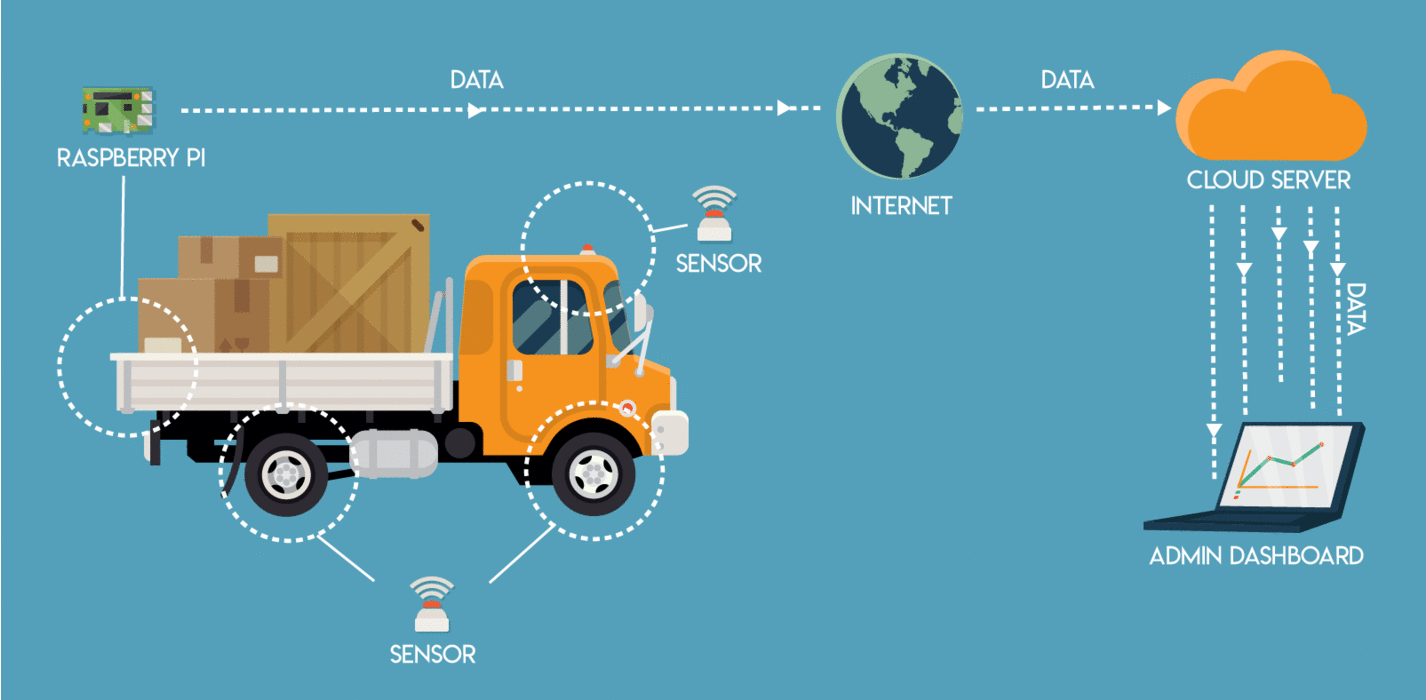
For tech enthusiasts and IoT developers, securing isolated, scalable, and efficient networks on small-scale devices has never been more accessible. With the rise of Remoteiot Free environments and Raspberry Pi-based edge platforms, setting up virtual private clouds (VPCs) enables developers to simulate isolated network topologies without physical infrastructure. This detailed guide reveals how to deploy and manage a Raspberry Pi VPC on Remoteiot Free, leveraging containerized networking tools—like Docker’s built-in VPC—ensuring secure, isolated communication for remote Internet of Things deployments.
At its core, a VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) on Raspberry Pi transforms a standard Linux device into a logically segmented network environment, mimicking enterprise-grade infrastructure at a fraction of the cost. Unlike public cloud VPCs, these lightweight virtual networks operate within constrained edge hardware, making them ideal for remote monitoring, smart agriculture, or industrial sensor networks. “The key advantage,” notes one embedded systems engineer, “is the ability to enforce network segmentation without resorting to physical routers—entirely within the Linux kernel.”
Why Raspberry Pi VPCs Are Ideal for Remote IoT Projects
Raspberry Pi platforms, particularly models like Pi 4 and Pi Zero W, offer the computing power and USB/ethernet connectivity needed for edge networking, paired with a software-defined perimeter that mirrors advanced cloud networking principles.When integrated with Remoteiot Free—an open-source platform simulating containerized IoT infrastructures—these devices become virtual VPC hosts capable of: - Creating isolated subnets for different sensor clusters or control groups - Enforcing secure communication using container-native networking, including svc-over-file and IPIP for encrypted data tunnels - Running lightweight yet robust firewall and routing rules inside Docker containers - Scaling dynamically with container orchestration via Docker Compose or Kubernetes (for larger deployments) These capabilities empower developers to prototype resilient, network-secured IoT systems without industrial-grade hardware.
Step-by-Step: Setting Up a Virtual Private Cloud on Raspberry Pi Using Remoteiot Free
The following workflow outlines how to establish a functional VPC environment on a Raspberry Pi integrated with Remoteiot Free, streamlined for remote network management.- Prepare the environment: Install Remoteiot Free on your host machine—available for ARM-based Raspberry Pis—and ensure system updates and Kernel 6.0+ or later are enabled for full compatibility with container networking.
- Configure the containerized network: Mount the `/pf_vpclib` volume inside a dedicated `docker-compose.yml` file to host the VPC’s container runtime. This directory houses `vpcd`—the virtual Ethernet switch acting as the network’s backbone.
- Deploy the VPC container: Run `docker-compose up -d` with a custom `vpCD` container image (or build one from minimal Linux with `iproute2` and IP-PIP utilities).
Map internal services to private subnets, assigning IP ranges via `/etc/docker/address-management.conf`.
- Establish secure subnet isolation: Use `ipakt` or `uarp` inside the container to assign static IPs and manage MAC addresses, enabling device-to-device isolation akin to VLAN tagging in enterprise networks.
- Integrate with IoT management tools: Connect the VPC to MQTT brokers or gRPC APIs within Docker, allowing secure message passing between gateways, microservices, and featherweight embedded clients.
Managing and Monitoring Your VPC: Best Practices and Real-World Tweaks
Effective VPC management transcends setup—it demands vigilance in monitoring traffic patterns, rerouting subnets dynamically, and patching configurations. Within Remoteiot Free, developers leverage lightweight monitoring agents (`vpcmon-collector`) running inside containers to parse packet logs, detect anomalies, and alert on bandwidth spikes.Rollback procedures must be predefined: Docker snapshots of VPC configurations allow rapid recovery after misconfigurations. “Consistency is king,” advises a network architect, “and in constrained Pi environments, every port, IP, and MAC address must be audited. Automation via Ansible playbooks synced with version control ensures reproducible, auditable deployments.” Key tools and practices include: - Regular inspection of `/sys/net/vpcd/routes` and `vpcd status` for routing integrity - Using Docker event streams (`docker events`) to track container lifecycle in real time - Application of eBPF filters for deep packet inspection without unpacking sensitive payloads - Segmented logging via `rsyslog` forwarding to remote S3 buckets or logging servers, enabling forensic analysis These strategies keep remote IoT networks resilient, scalable, and aligned with zero-trust principles.
The Power of Raspberry Pi VPCs: Redefining Edge Networking at Scale
The integration of Raspberry Pi-based virtual private clouds within Remoteiot Free environments marks a paradigm shift in how remote IoT systems are designed and maintained. No longer limited to simple star topologies, modern edge deployments now harness lightweight, containerized networking to achieve enterprise-grade isolation, security, and manageability—all within a $35 hardware unit. As IoT expands into agriculture, smart cities, and industrial automation, mastering tools like Raspberry Pi VPCs ensures developers can build scalable, reliable, and future-ready networks, one micro-device at a time.The future of edge networking is here—and it’s smaller, smarter, and profoundly accessible.


Related Post
Karin Reznack Age Wiki Net worth Bio Height Husband

Tom Hollander’s Height Revealed: How Stature Supports a Legendary Actor’s Magic on Screen

