Master Math with the 30-60-90 Triangle: Your Key to Mastering Right Triangles
Master Math with the 30-60-90 Triangle: Your Key to Mastering Right Triangles
At the heart of trigonometry lies a deceptively simple geometric truth: the 30-60-90 triangle—a right triangle with angles of 30°, 60°, and 90° that unlocks powerful tools for solving complex spatial problems. From architectural blueprints to physics formulas, this triangle offers a reliable structure that simplifies calculations and reveals deeper insights into angle relationships. Whether you’re a student grappling with trigonometric fundamentals or a professional navigating technical drawings, understanding this triangle accelerates learning and enhances precision.
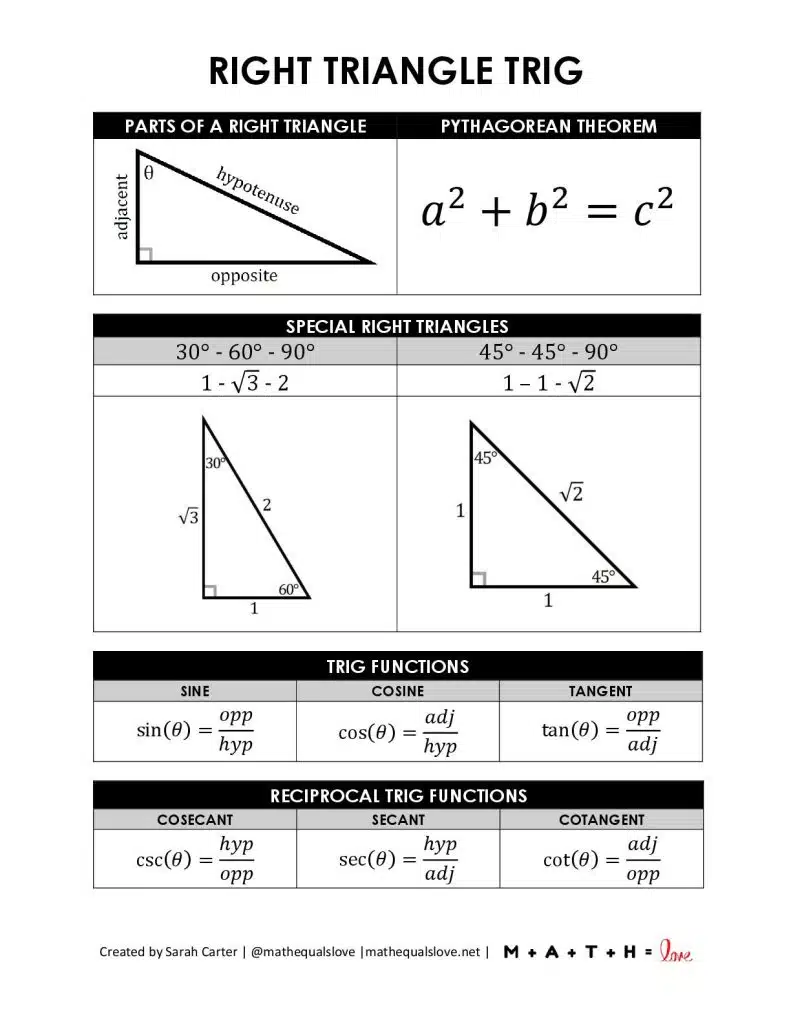
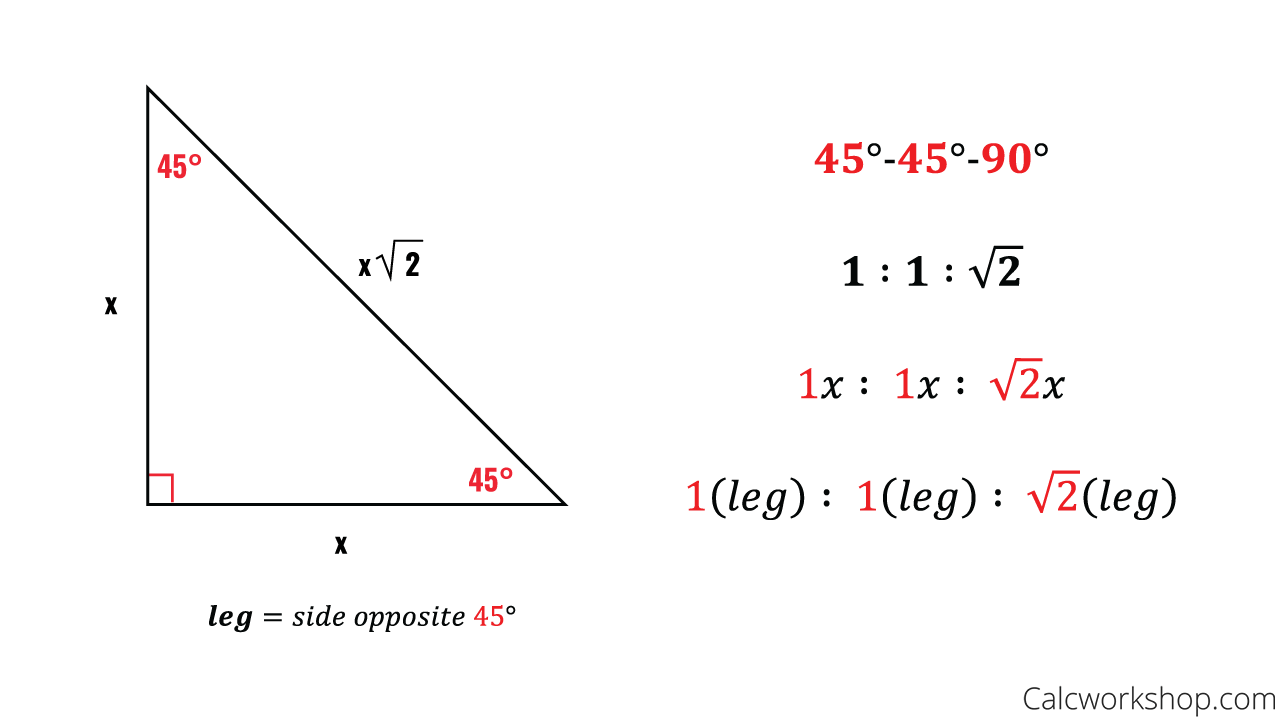
The 30-60-90 triangle is defined by its distinctive angle pattern: the smallest angle is 30°, its complement is 60°, and the right angle measures 90°.This configuration produces consistently predictable ratios among the side lengths, making it indispensable for applications ranging from construction to electrical engineering. The triangle’s symmetry and trigonometric consistency stem from its foundation in equilateral triangle properties, where splitting a 60° angle yields two 30° angles and cascading 30-60-90 relationships emerge naturally. Each side of the triangle follows a precise, shareable ratio: the shortest leg (opposite 30°) is 1 unit, the long leg (opposite 60°) measures √3 units, and the hypotenuse (opposite 90°) equals 2 units.
This 1 : √3 : 2 proportion eliminates guesswork and enables rapid computation without relying on universal calculators. The enduring relevance of these ratios traces back to ancient Greek geometry, where early mathematicians like Hippocrates of Chios laid groundwork later refined through Islamic and Renaissance scholarship. For anyone aiming to build confidence in geometry, the 30-60-90 triangle serves as a foundational building block.
It bridges basic triangle recognition with advanced angle and side trigonometry, allowing learners to decompose complex shapes into manageable segments.
In practical terms, the 30-60-90 triangle transforms abstract angle measurements into concrete lengths, enhancing accuracy in real-world scenarios. Its ratios empower engineers calculating load distributions in triangular trusses, architects aligning diagonal supports, and educators creating visual aids for classroom instruction.
Unlike more complex triangles, this design boasts symmetry that preserves proportionality regardless of orientation—a trait often missing in irregular or arbitrary triangles.
The ratios offer immediate benefits during calculation:- With the hypotenuse known (2 units), the 30° opposite side measures 1 unit—simply divide the hypotenuse by 2.
- The 60° opposite leg, √3, is derived by multiplying the short leg (1) by √3, avoiding equation-solving.
- Once one side is determined, the others follow instantly via known proportions.
These relationships are not mere conventions—they reflect deep geometric consistency. When a right triangle splits into 30° and 60° angles via a height or median, the resulting 30-60-90 structure ensures ratios remain intact, enabling real-time problem-solving without re-derivation.
Visually, the triangle’s balance—with one leg half the hypotenuse and √3 times the shorter—creates a pyramid of proportions easy to memorize and apply. Students often cite this clarity as a turning point in mastering trigonometric concepts.As one engineering student noted, “Understanding the 30-60-90 triangle didn’t just simplify my homework—it redefined how I see geometry as a language of space.” Designing effective learning materials around this triangle reveals its versatility. Diagrams with labeled sides, side-length tables, and deriving ratios step-by-step reinforce muscle memory and visual intuition. “Diagrams aren’t just illustrations—they’re cognitive scaffolding,” explains Dr.
Elena Ruiz, professor of applied mathematics. “Seeing the 1:√3:2 ratio plotted consistently cements understanding far faster than symbolic formulas alone.” The triangle’s edge extends beyond classroom science. In physics, it aids vector decomposition—resolving forces along 30° and 60° axes simplifies motion analysis in mechanics.
In architecture, triangular trusses leverage these ratios to evenly distribute weight across structures, enhancing stability and material efficiency. Electrical engineers use similar proportions in calculating impedance triangles for AC circuits, where phase angles mirror 30° and 60° behavior. Moreover, the 30-60-90 triangle acts as a gateway to advanced trigonometry.
Its ratios form the basis for understanding sine and cosine values in standard angles, and later, for navigating polar coordinates and complex numbers. For professionals, fluency in such foundational constructs means faster adaptation to specialized tools and faster error detection in complex models. The enduring appeal lies in its simplicity and universality.
Whether scaled up in skyscrapers or scaled down in classroom exercises, the 30-60-90 triangle remains a trusted reference. Its pre-defined ratios provide reliability in uncertain measurements, reducing calculation drift and enhancing consistency across assignments and projects. In a world where precision matters, this triangle delivers both accuracy and clarity.
For students and professionals alike, mastering the 30-60-90 triangle is more than learning a formula—it’s gaining a spatial framework that transforms abstract angles into tangible, predictable relationships. From balancing forces in a bridge to calculating signal latitudes in electrical waves, this triangle proves time and again: geometry, when understood deeply, is not just theoretical—it’s transformative.


Related Post

Through the Lens of Time: The Impact of Winning Time Cast on Modern Storytelling
[GROUNDBREAKING] Revelations Surrounding Michael Ealy Parents: Unveiling Familial Roots and Influences

