Osmosis Unlocked: How Nature’s Quiet Membrane Mechanism Powers Life, Medicine, and Industry
Osmosis Unlocked: How Nature’s Quiet Membrane Mechanism Powers Life, Medicine, and Industry
Osmosis, the silent flow of water across selective barriers, governs fundamental biological processes and underpins innovations across medicine, agriculture, and environmental technology. Far more than a laboratory curiosity, osmosis shapes the way cells absorb nutrients, how plants draw water from soil, and why desalination plants function. By understanding its real-world applications, we gain insight into nature’s elegant engineering—and humanity’s growing mastery of it.
Osmosis explained is simple at its core: water molecules move from regions of lower solute concentration to higher solute concentration through a semi-permeable membrane, striving to achieve equilibrium. This passive transport requires no energy input, yet drives essential functions from cellular hydration to industrial purification. Unlike active transport, which demands cellular energy, osmosis operates with remarkable efficiency, making it indispensable in both living organisms and engineered systems.
The Biological Clockwork: Osmosis in Human Cells
Within each human cell lies a dynamic equilibrium maintained by osmosis. The cell membrane, a lipid bilayer studded with embedded proteins, acts as a precise filter—allowing water but restricting dissolved solutes. When cells absorb water via osmosis, they swell in a controlled manner, preserving structure and function.Conversely, excessive solute exposure forces water out, risking shrinkage that compromises cellular processes. In kidney function, osmosis enables selective reabsorption of water from filtered urine. “The kidneys fine-tune hydration by adjusting solute concentration in tubule fluid,” explains Dr.
Elena Torres, a renal physiologist. “Water follows, reclaiming vital fluids while eliminating waste—an osmotic ballet regulated by hormones like antidiuretic hormone.” This process sustains blood volume and electrolyte balance, highlighting osmosis as life’s microscopic lifeline. Plant cells rely equally on osmotic pressure.
Known as turgor pressure, the inward push of water maintains stem rigidity and leaf posture. “Without osmosis, plants would wilt at the first sign of dehydration,” notes botanist Marcus Lin. Roots absorb water from soil; if the root cells’ internal solute concentration is balanced, water enters.
When soil dries, solute levels rise, drawing moisture from deeper tissues—a mechanism vital for drought resilience and crop yield. “Tailoring solute concentrations prevents cellular lysis or shrinkage—critical for patient safety,” warns Dr. Priya Mehta, a clinical pharmacologist. Osmotic intravenous hydration now forms the foundation of emergency rehydration protocols, from treating dehydration to optimizing drug delivery. Real-World Innovation: Osmosis in Medicine and Water Treatment Beyond biology, osmosis powers life-saving technologies. Osmotic pressure drives reverse osmosis filtration, a cornerstone of modern desalination. By forcing seawater through semi-permeable membranes under pressure, salt and impurities are separated, producing fresh water. “Reverse osmosis has transformed arid regions,” observes Dr. Rajiv Nair, environmental engineer. “It provides clean drinking water where traditional sources are scarce—elevating millions of lives.” In medicine, osmotic gradients ensure precise drug delivery. Nanocarriers exploit osmotic forces to release therapeutic payloads at target sites. “Smart drug systems mimic natural osmotic mechanisms,” explains Dr. Nair. “This allows controlled release without invasive procedures—turning osmosis into a gateway for targeted treatment.” In agriculture, researchers design osmotic barriers to conserve water. Hydrogel nanoparticles absorb and slowly release moisture, reducing irrigation needs in drought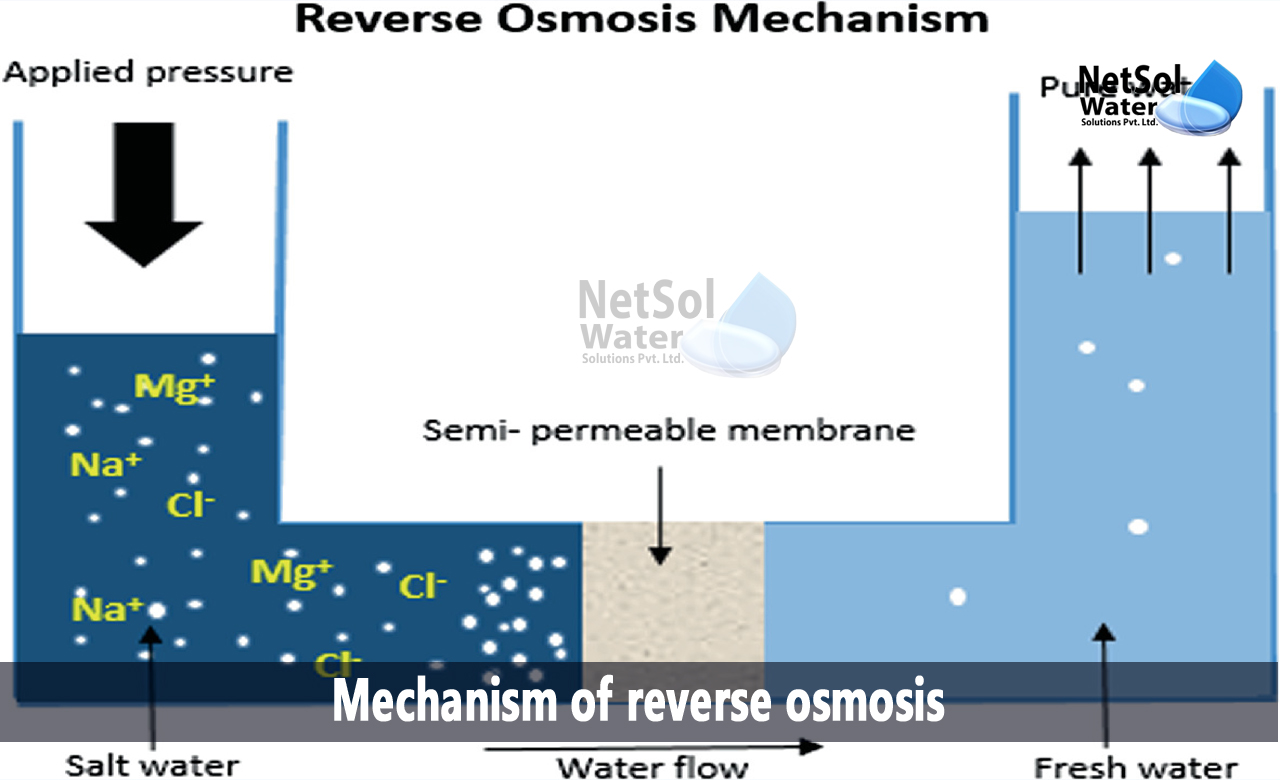



Related Post

Master All Roles in Town of Us Among Us Mod: The Complete Guide to Town Dynamics

Bianca Censori’s Grammy Dress: A Masterpiece of Red Carpet Elegance

Maryland Football History: A Legacy Of Terps Football Defining a Quarterback Dynasty and College Pride

The Age Of Adaline Cast

