<strong>Revolutionizing Urban Living: The Hidden Power of Smart Infrastructure News</strong>
Revolutionizing Urban Living: The Hidden Power of Smart Infrastructure News
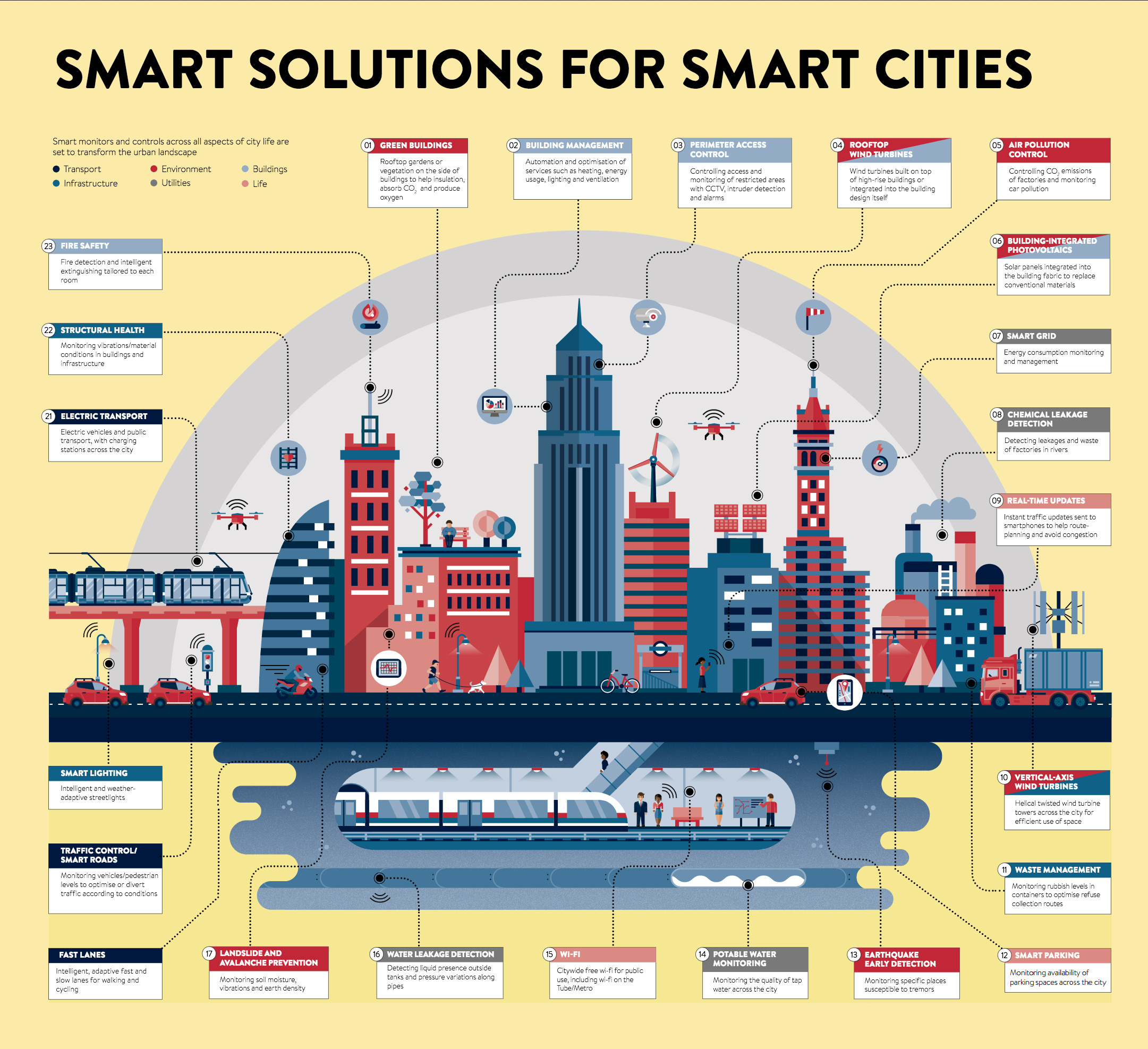
Global cities are undergoing a silent transformation—driven not by grand monuments or flashy tech launches, but by intelligent, interconnected infrastructure redefining how millions live, move, and engage. Smart infrastructure—defined by data-driven systems embedded in urban environments—is emerging as the backbone of sustainable, efficient, and resilient metropolitan life. From adaptive traffic lights reducing congestion to AI-powered energy networks balancing demand, this silent revolution is already reshaping headlines and daily routines across the world’s largest cities.
At the heart of this transformation is the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors with artificial intelligence and real-time analytics. These technologies allow cities to monitor and manage assets, energy use, public transport, and environmental conditions dynamically. “We’re no longer just building cities—we’re building responsive ecosystems,” says Dr.
Elena Torres, urban technologies expert at MIT’s Senseable City Lab. “Every street, building, and utility is a node in a vast, learning network that anticipates needs before they arise.”
Key deployments illustrate the tangible impact. In Singapore, for instance, smart sensor arrays embedded in roadways and waterways track traffic flow, air quality, and structural health with millisecond precision.
This data feeds city command centers that adjust traffic signals in real time—reducing average commute times by as much as 22% during peak hours.1 Similarly, Barcelona’s smart lighting grid uses motion detection and ambient light sensors to dim or brighten streetlights, cutting energy consumption by nearly 40% while maintaining public safety.
Beyond traffic and energy, smart infrastructure is driving health and equity gains. New York City has rolled out adaptive traffic crossings around schools during drop-off and pick-up times, significantly improving pedestrian safety.2 In Amsterdam, predictive maintenance systems monitor bridges and tunnels, detecting early signs of wear and scheduling repairs before failures occur—extending infrastructure lifespan and reducing costly disruptions.
What makes this revolution distinguishable is its data-centric, adaptive nature. Traditional urban planning relied on static models and historical trends, but modern smart systems evolve continuously, learning from real-world patterns. This agility enhances resilience against disasters, climate volatility, and sudden shifts in population density or mobility behavior.3 “The future of cities isn’t about bigger or faster—it’s about smarter,” notes Amir Nasr, CTO of IoTeX, a global smart infrastructure firm.
“Infrastructure that thinks and adapts becomes the ultimate urban asset.”
Real-world deployments emphasize scalability and inclusivity. Seoul’s Smart City initiative integrates low-cost sensors across informal neighborhoods, bridging the digital divide by extending high-tech benefits to underserved communities. In Nairobi, adaptive water distribution networks use AI to predict and prevent leaks, cutting non-revenue water by 35% and improving access in rapidly expanding slums.4 These examples underscore a critical principle: smart infrastructure must be accessible, interoperable, and rooted in local needs.
Security and privacy remain central concerns. As cities collect vast amounts of data, robust encryption, transparent governance, and citizen consent frameworks are essential to maintain trust. Barcelona leads by design, embedding privacy-by-default protocols into every layer of its smart grid.
“Technology should empower, not intrude,” asserts Ericha Valdez, the city’s Digital Rights Commissioner. “We’re building systems where data protection is non-negotiable, and citizens remain in control.”
Looking ahead, the convergence of smart infrastructure with emerging technologies promises even greater leaps. Autonomous public transit, driven by real-time optimization and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication, is being tested in cities like Helsinki and Phoenix.
Meanwhile, blockchain-powered energy markets in Oslo allow households to trade solar power directly, decentralizing the grid and boosting renewable adoption. 5 These developments align with global sustainability goals, positioning smart infrastructure as a linchpin of climate action.
From reducing congestion to enhancing public health and strengthening equity, smart infrastructure is rewriting urban narratives.
As adoption accelerates, cities are transforming from static hubs into living, breathing systems—responsive, sustainable, and uniquely attuned to their people. The next chapter of urban development isn’t just intelligent; it’s inherently adaptive. For decision-makers, developers, and citizens alike, the message is clear: infrastructure is no longer built—it’s built to evolve.
In an age where urbanization accelerates and climate pressures mount, smart infrastructure stands as a beacon of progress. Its quiet revolution is already shaping skylines, streets, and lives—one data point at a time. This is infrastructure reimagined: not as steel and concrete, but as a dynamic, living network designed to serve humanity.
The future city isn’t arriving—it’s already here.
References: 1> Singapore Smart Nation Sensor Insights, 2024. 2> NYC DOT Traffic Safety Report, Q2 2023.3> Resilience Institute Global, “Adaptive Infrastructure”、“2024 Urban Resilience Review.” 4> Seoul Metropolitan Government, “Smart Water Management Annual Report.” 5> Oslo Energy Market Pilot, National Grid Lab, 2023.



Related Post

Stay Updated: Why Timely Information Is Your Secret Weapon in Today’s Fast-Paced World

Navers Unveils Game-Changing Updates: What’s Driving the Tech Giant’s Latest Innovation Surge?

Seo News Whats New And What You Need To Know in 2024
What Every CNA Should Know About This One Weird Trick and the Hidden Power of POC Login Access

