Stakeholder Engagement: The Definitive Guide to Aligning Interests for Sustainable Success
Stakeholder Engagement: The Definitive Guide to Aligning Interests for Sustainable Success
In today’s interconnected world, organizational outcomes hinge not on isolated decisions but on the active involvement of diverse stakeholders. Stakeholder engagement transcends mere consultation—it is a strategic, iterative process that identifies, communicates with, and includes individuals and groups affected by or influencing a project, policy, or initiative. When executed strategically, it transforms potential resistance into collaboration, turning diverse voices into shared momentum.
As Dr. Maria Lopez, a renowned governance consultant, notes: “True engagement doesn’t demand consent—it builds trust through listening.” This guide explores how structured stakeholder engagement empowers decision-makers to navigate complexity, anticipate risks, and unlock collective value across sectors.
From community residents and employees to investors and regulators, each stakeholder group brings unique insights, expectations, and influence.
Understanding these perspectives isn’t optional—it is foundational to responsible and effective governance. A 2023 Global Engagement Survey revealed that organizations prioritizing stakeholder input report 37% higher project success rates and 52% reduced risk exposure. This article dissects the core principles, frameworks, and practical tactics that turn engagement from a box-ticking exercise into a strategic advantage.
Why Stakeholder Engagement Matters: More Than Public Relations
At its core, stakeholder engagement is about recognizing that stakeholders are not passive recipients of organizational actions but active agents shaping outcomes. Their support or opposition directly impacts implementation speed, compliance, reputation, and long-term viability. Projects that neglect this dynamic often face delays, opposition, or even outright failure.-stakeholders provide critical contextual intelligence that no internal analysis can replicate. Frontline employees understand operational realities; local communities grasp cultural nuances; investors assess financial implications. Beyond information, stakeholders bring accountability.
When communities feel heard, they are more likely to advocate for a project rather than challenge it. -*“Silencing stakeholders breeds distrust; engaging them builds resilience,”* says James Chen, director of governance at a leading multinational corporation. This sentiment underscores engagement’s role in risk mitigation and relationship capital.
Stakeholder mapping is a foundational step. Identifying stakeholders by influence, interest, and impact allows organizations to tailor engagement strategies. For example, regulatory bodies require transparent, formal communication, while local residents may respond best to face-to-face dialogue and participatory forums.
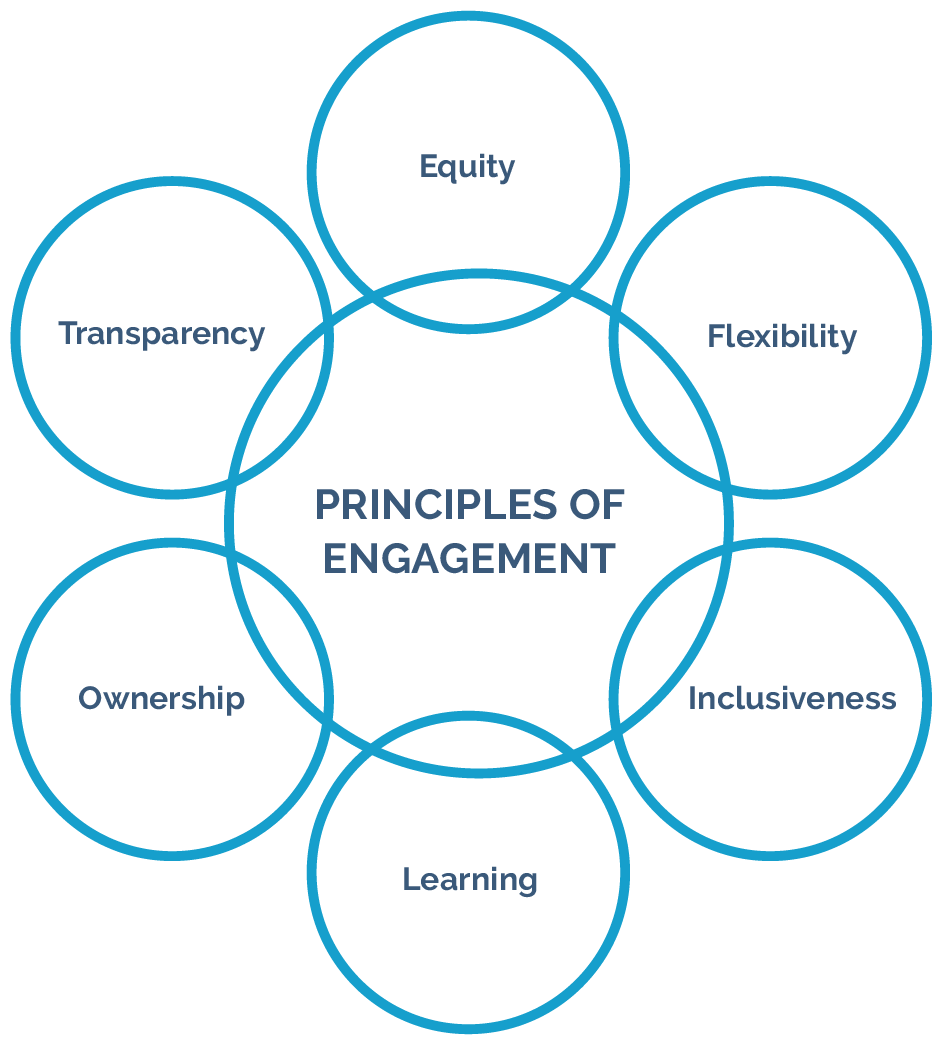
Key Principles of Effective Stakeholder Engagement
Successful engagement rests on several guiding principles that ensure authenticity, inclusivity, and impact. -Transparency forms the bedrock. Stakeholders must understand why decisions matter, what voices are included, and how input influences outcomes.Regular, honest updates prevent misinformation and build credibility. As Dr. Patricia Reed, professor of public policy, notes: “Transparency isn’t about sharing everything—it’s about sharing what matters.” -Inclusivity demands intentional outreach to underrepresented groups, ensuring participation reflects the full spectrum of affected parties.
Excluding key stakeholders risks missing critical concerns and undermining legitimacy. -Accessibility means designing engagement processes that accommodate different backgrounds, languages, and abilities. Remote communities, non-native speakers, and individuals with disabilities should not face barriers to participation.
-Reciprocity emphasizes two-way dialogue over monologue. Stakeholders give input; organizations respond meaningfully. This mutual exchange fosters long-term partnership rather than transactional compliance.
-Adaptability keeps engagement alive and responsive. As circumstances evolve—policy shifts, emerging crises, or new stakeholder needs—processes must adjust. Rigid plans risk irrelevance; flexibility ensures ongoing alignment.
Core Steps in Structured Stakeholder Engagement
A well-designed engagement framework follows a cyclical process that integrates preparation, action, evaluation, and iteration.Tools like power-interest grids help visualize priorities. A municipality rolling out a green energy initiative, for example, must distinguish between utility providers (high power, high interest), environmental NGOs (high interest, moderate power), and residents (moderate interest, variable influence).
Prioritize Engagement Based on Risk and Value Not all stakeholders deserve equal attention. A risk-based approach identifies those whose support or opposition could derail progress—such as regulatory authorities or key community leaders. High-risk groups often require deeper investment in consultation and trust-building.
Digital platforms can scale outreach but should complement—not replace—personal connection.
Active listening, inclusive dialogue, and timely follow-up are essential. Organizations that treat stakeholders as partners—rather than noise—create psychological safety for honest input.
Monitor, Evaluate, and Adapt Data collection—through feedback forms, sentiment analysis, or retention rates—tracks engagement effectiveness. Regular review ensures the process evolves with stakeholder expectations and organizational goals. Metrics like participation rates, issue resolution speed, and trust indicators provide actionable insights.
Real-world success stories illustrate these principles. A major infrastructure project in Southeast Asia integrated Indigenous communities early, using local mediators and culturally appropriate forums. This approach reduced delays by 40% and secured community endorsement, transforming potential conflict into shared ownership.
Similarly, a European healthcare provider used digital pulse surveys to adapt patient engagement in real time, improving service uptake and satisfaction.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Stakeholder Dynamics
Despite its benefits, stakeholder engagement faces persistent obstacles. Conflicting interests often arise—for example, economic benefits for investors versus environmental concerns for activists.Mediating such tensions demands neutral facilitation, creative problem-solving, and sometimes trade-offs. Combating Apathy and Misinformation Not all stakeholders are eager to participate. Passive or negative attitudes may stem from past exclusion or misinformation.
Proactive outreach, clear messaging, and visible action on feedback build motivation. Organizations should anticipate skepticism by demonstrating responsiveness—showing stakeholders their voices lead to tangible change. Managing Power Imbalances Hierarchies and unequal access to resources can skew engagement.
Meaningful inclusion requires intentional efforts to amplify marginalized voices, such as dedicated listening sessions or third-party advocacy. Without counterbalancing mechanisms, dominant stakeholders may overshadow quieter yet critical perspectives. Ensuring Sustainability Short-term campaigns often falter when engagement efforts end once deliverables are met.
Sustained engagement embeds stakeholder rhythms into governance—quarterly forums, permanent advisory councils, or embedded Feedback Loops ensure continuous alignment and trust.
Tools and Technologies Enhancing Engagement Practices
Technology amplifies stakeholder reach and depth. Digital platforms enable scalable data collection—online polls, chatbots for real-time input, and collaborative tools like Miro or Slack for ongoing dialogue.GIS mapping visualizes community sentiment geographically, while AI-driven sentiment analysis identifies emerging concerns in social media or feedback channels.
_blockchain-based consent systems are emerging as tools for transparent, auditable engagement records. While still niche, such innovations promise greater accountability in high-stakes projects involving sensitive data or multiple rights-holders.
Regardless, the human element—empathy, dialogue, and mutual respect—remains irreplaceable.
Best Practices for Sustained Engagement
Successful stakeholder engagement is not a one-time event but an ongoing discipline. Key best practices include:1.
Start Early, Not Just at Critical Moments Engagement must begin at concept development, not during crises or final approvals. Early involvement shapes design, prevents costly revisions, and builds stakeholder buy-in before decisions harden.
2.
Foster Two-Way Communication, Not One-Sided Reporting Share decisions transparently, but actively solicit and document feedback. Integrate insights into planning, and communicate how input influenced outcomes—this closes the loop and reinforces trust.
3.
Build Long-Term Relationships, Not Transactional Encounters Treat stakeholders as partners through consistent touchpoints—quarterly updates, advisory panels, or joint problem-solving teams. Relationships built on reliability outlast any single project.
4.
Measure Impact with Clear Metrics Track both quantitative indicators (participation rates, engagement satisfaction scores) and qualitative shifts (trust levels, collaborative outcomes). These metrics not only assess performance but guide continuous improvement.
5.
Invest in Capacity, Not Just Tools Equip teams with training in facilitation, cultural sensitivity, and conflict resolution. Stakeholder engagement thrives when people—not just platforms—drive the process.
The Transformative Power of Stakeholder Engagement
Stakeholder engagement is far more than a compliance checkbox or PR tactic—it is the cornerstone of resilient, responsible, and effective decision-making.When organizations embrace it as a core strategic capability, they unlock innovation, reduce risk, and build enduring trust. As leadership expert Robert Greenhalgh observes: “Engagement isn’t about pleasing everyone—it’s about empowering everyone to shape what matters.” In a world facing complex, interdependent challenges, the ability to listen, include, and collaborate defines leaders. This comprehensive guide provides the frameworks, tools, and insights needed to transform stakeholder engagement from a challenge into a competitive advantage—one conversation at a time.


Related Post

Daviess County Man Captured in Wide-Meaner Mugshot—Community Urges Vigilance as Police Close in on Wanted Fugitive

Komik Tentang Kesehatan Anak Sehat: Lebih Dari Separuh Kejatoruan dengan Seksi Bersama Dr Dian Sahabat Gema Insani
The Untold Truth About Will Levis Gia Duddys Relationship: A Gripping, Unexpected Story You Won’t Believe

How Paradise By Coldplay Defined Empathetic Rock Through Sound and Story

