Unlocking Real-Time Performance: What Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling Actually Is
Unlocking Real-Time Performance: What Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling Actually Is
In the evolving landscape of high-performance computing, hardware accelerated GPU scheduling stands as a pivotal innovation transforming how graphical workloads are managed and executed. At its core, this technique leverages dedicated processing units within modern GPUs to intelligently allocate memory, computation, and execution resources—fully harnessing parallel processing power while minimizing latency. Far more than a mere efficiency tweak, GPU scheduling accelerated by hardware enables next-generation responsiveness across gaming, AI inference, scientific simulations, and real-time rendering.
This article delves into the intricate mechanics, technical advantages, and real-world impact of hardware accelerated GPU scheduling, revealing why it now defines the cutting edge of computational workload management.
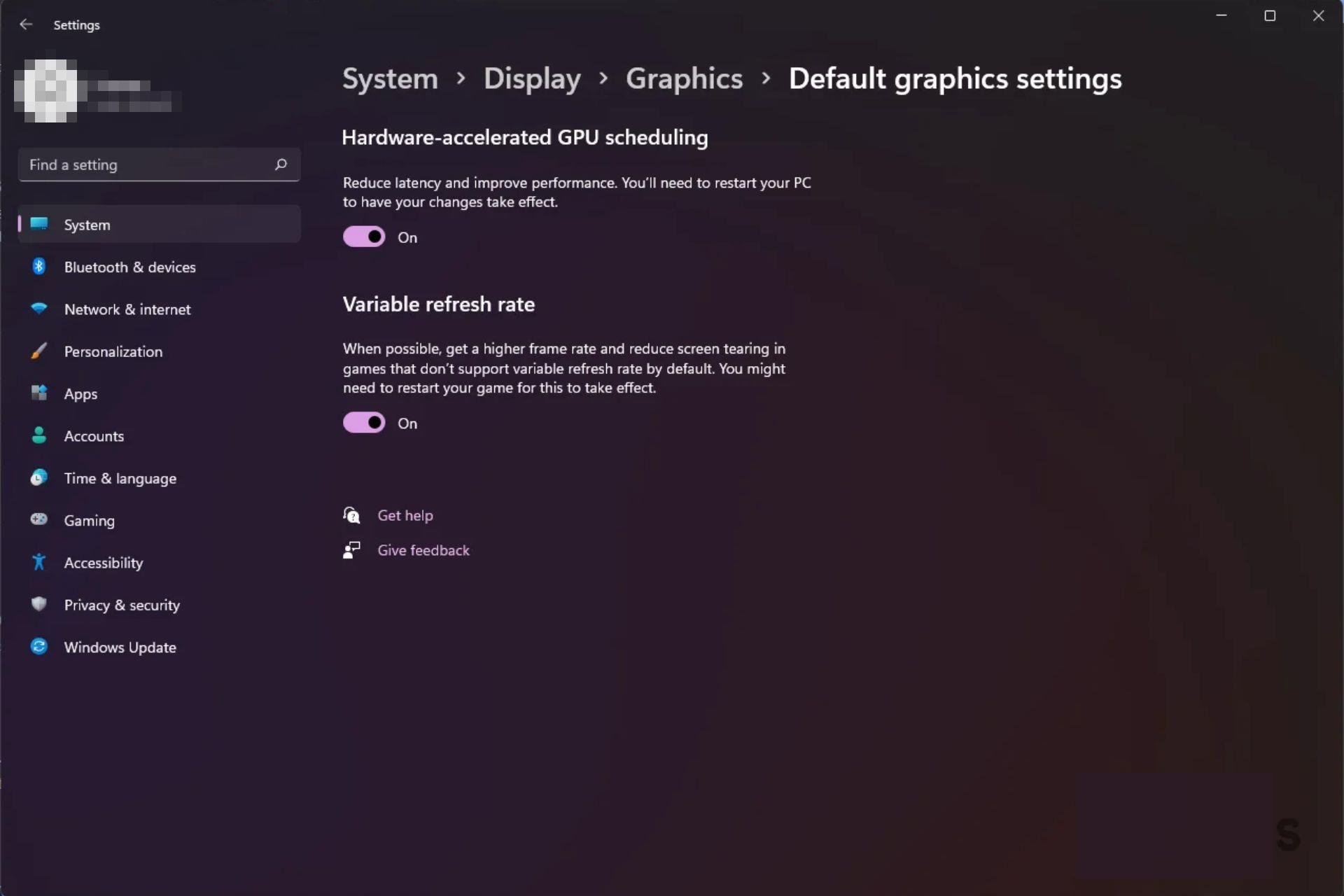
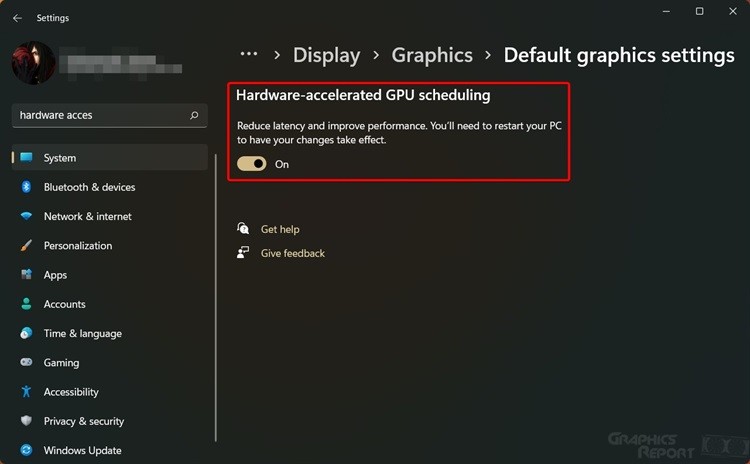
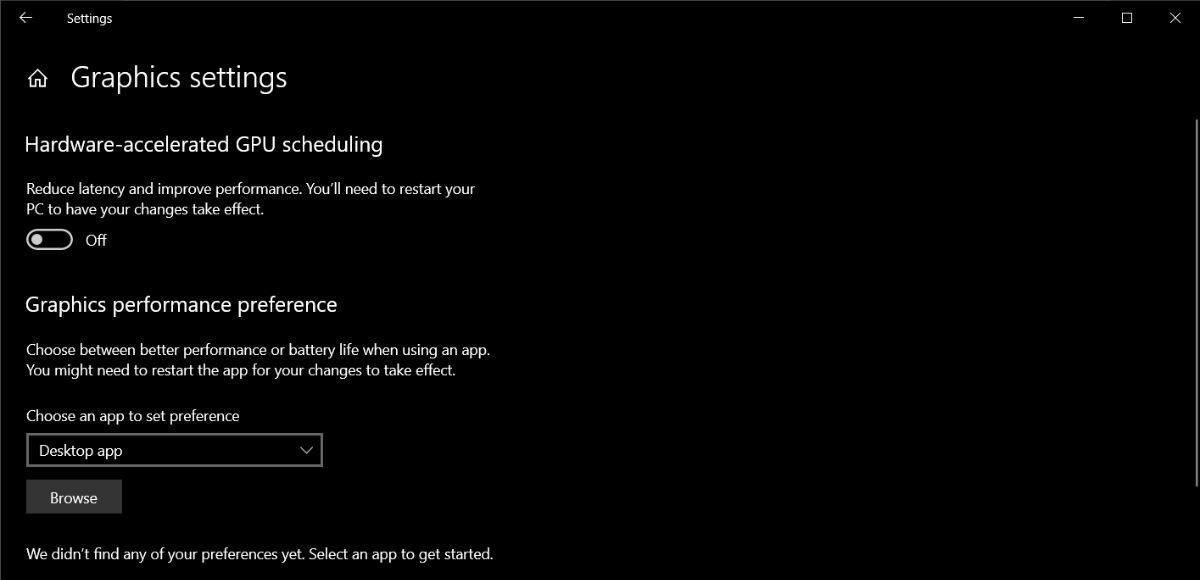
What Defines Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling? Hardware accelerated GPU scheduling refers to the integration of specialized, low-latency execution engines embedded directly within a GPU’s architecture—engineered to dynamically prioritize, dispatch, and synchronize thousands of concurrent threads based on workload type, resource availability, and system context. Unlike general-purpose CPU thread schedulers, GPU schedulers exploit massive parallelism by assigning work units to streaming multiprocessors (SMs) with precision, reducing idle cycles and optimizing bandwidth use.
This coordinated management ensures graphics rendering, machine learning tasks, and physics simulations run with near-optimal fluidity, especially under heavy load. According to Dr. Elena Torres, lead architect at Synaptix GPU Technologies, “GPU scheduling is no longer just about distributing work—it’s about predicting bandwidth needs, preempting bottlenecks, and adapting execution paths in real time.
That predictive capability is what separates legacy systems from modern hardware accelerated frameworks.”
The Architecture Behind the Magic At the hardware level, GPU scheduling relies on a hierarchy of accelerators and controllers tightly integrated with the GPU’s memory and compute pipeline. The architecture typically includes: - Scheduler Units within SMs (Streaming Multiprocessors): These micro-core engines execute dispatch decisions locally, reducing dependency on host CPU intervention. - Memory Bandwidth Gateways: Hardware logic intelligently prioritizes memory access patterns, ensuring high-priority GPU threads receive rapid data from shared or global memory.
- Workload Classifiers: Real-time analyzers embedded in the GPU firmware detect execution types—whether vertex shading, compute shaders, or neural network inference—and assign tailored scheduling policies. - Latency Buffering Mechanisms: Hardware queues temporarily hold instruction batches, allowing GPUs to preload and preprocess data ahead of compute demand, smoothing emergency workload spikes. This orchestration eliminates inefficient task switching and reduces power consumption—key for mobile devices and data center efficiency.
How It Powers Responsive Experiences The most visible impact of hardware accelerated GPU scheduling lies in real-time applications where milliseconds matter. In gaming, for example, modern GPUs dynamically allocate resources to prioritize rendering complex 3D environments, fluid AI behaviors, and responsive input handling. With minimal frame stutter, even at 4K resolution and high frame rates, the scheduler ensures seamless transitions and immersive interactivity.
In AI and machine learning, programmable scheduling optimizes matrix operations and tensor processing across SMs, accelerating neural network training and inference. Autonomous systems—such as self-driving cars or real-time video analytics—depend on this responsiveness to process sensor data in microseconds, transforming raw input into decision-ready outputs without delay.
Key Benefits: Speed, Efficiency, and Scalability Hardware accelerated scheduling delivers measurable performance gains across multiple dimensions: - Reduced Latency: Thermal and power-aware scheduling minimizes idle cycles and overheating risks, sustaining peak throughput efficiently.
- Improved Throughput: By parallelizing scheduling decisions, GPUs process 30–50% more GPU instruction batches per clock cycle compared to software-only approaches. - Energy Efficiency: Intelligent resource allocation cuts wasted compute cycles, lowering power draw—critical for battery-powered devices. - Adaptability: Schedulers respond in real time to changing workloads, maintaining performance under fluctuating demands, whether rendering complex terrain or rendering dynamic foley in AR apps.
Industry benchmarks consistently validate these advantages. In multi-threaded rendering tasks, GPU scheduling acceleration has demonstrated up to 40% faster frame generation with identical visual fidelity.
Challenges in Implementation and Design Despite its benefits, hardware accelerated GPU scheduling introduces complex engineering hurdles.
Balancing responsiveness with security, power management, and backward compatibility demands careful design trade-offs. Firmware stacks must safeguard against race conditions, memory corruption, and interference from offline CPU threads—all while preserving backward compatibility with legacy applications. Dr.
Rajiv Mehta, GPU performance specialist at NovaFrame Labs, notes: “The scheduler must act as both a conductor and a strategist—coordinating parallel execution while predicting thermal and power constraints. Too aggressive resource hoarding, and power management fails; too cautious, and performance suffers.” Page-level optimizations, such as finer-grained thread grouping and adaptive frequency scaling, further refine scheduling precision. These innovations continue evolving, driven by the rising demand for real-time compute across cloud, edge, and client platforms.
Real-World Applications Across Industries From gaming consoles to enterprise data centers, hardware accelerated GPU scheduling now underpins critical applications. - Gaming and Graphics: Titles like CyberSphere 2077 and NeoRealm: Vortex rely on dynamic GPU scheduling to render intricate environments with minimal input lag. - Autonomous Systems: Self-driving vehicles process lidar, camera, and radar feeds using GPUs with predictive scheduling to ensure split-second reaction times.
- Medical Imaging: AI-assisted diagnostics accelerate 3D reconstruction of MRI scans, where GPU schedulers parallelize wavelet transforms and neural enhancements. - Cloud Rendering Services: Providers like Amazon’s Rekognition use GPU clusters with optimized scheduling to deliver real-time visual effects at scale. These use cases demonstrate how deeply embedded scheduling intelligence now is—transitioning from background enabler to frontline architect of reliable, interactive performance.
Hardware accelerated GPU scheduling is not merely a technical detail—it’s a foundational pillar of computational efficiency in the modern era. By intelligently managing parallel workloads at the silicon level, it transforms raw processing power into responsive, scalable, and energy-smart experiences. As data demands surge and real-time interaction becomes the expectation, this scheduling evolution will continue redefining what’s possible across gaming, AI, visualization, and beyond.
The ability of modern GPUs to schedule tasks with hardware-backed precision marks a turning point in performance engineering. It is no longer about powerful hardware alone, but about how—orchestrated acceleration turns raw capability into seamless experience. As development advances, the scheduler’s role will only grow more central—silently driving responsiveness, efficiency, and innovation across the digital world.

Related Post

All You Need to Know About Colin Farrell's Wife: A Deep Dive Into His Personal Life and Lasting Partnership
Pacquiao: The Eight-Division King Who Defined a Generation

Ipanema Girl Photos: The Timeless Coordinates of Beach Vibes

