Unlocking Seamless Integration: Web API in ASP.NET Core Explained Simply
Unlocking Seamless Integration: Web API in ASP.NET Core Explained Simply
Web APIs serve as the backbone of modern web applications, enabling smooth communication between client-side interfaces and backend services. In ASP.NET Core, developers gain a powerful, lightweight, and highly efficient framework for building and consuming Web APIs—combining performance, scalability, and seamless integration with the .NET ecosystem. This article breaks down the core concepts, practical implementation, and architectural advantages of Web API in ASP.NET Core for developers seeking to build robust, tomorrow-ready applications.
What Is a Web API in ASP.NET Core?
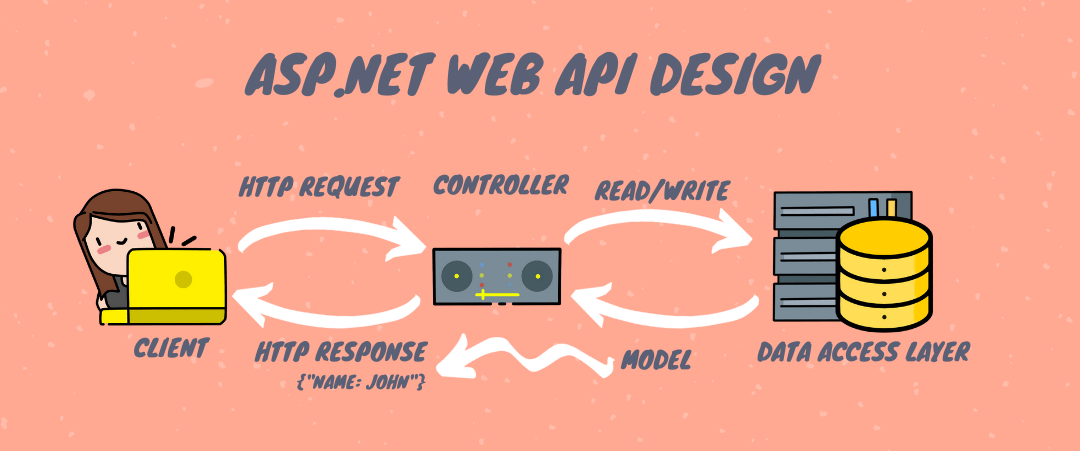
At its core, a Web API in ASP.NET Core is a framework for designing RESTful services that expose endpoints to handle HTTP requests and return structured data—typically in JSON or XML formats.
Unlike traditional full-stack MVC architectures, ASP.NET Core Web API focuses on building scalable backend services optimized for decoupled client applications, such as single-page apps (SPAs), mobile apps, or microservices.
Built on the foundation of .NET’s Minimalist Architecture, Web API leverages advanced middleware, dependency injection, and model-binding capabilities to streamline development. According to Microsoft documentation, “ASP.NET Core Web API is designed to be minimal yet feature-rich, reducing boilerplate while enabling high performance through optimized runtime components.” This balance makes it a preferred choice for backend engineers aiming to deliver responsive, secure, and maintainable APIs.
The Architectural Edge: Scalability and Flexibility
One of the defining strengths of Web API in ASP.NET Core is its architectural flexibility. Unlike more rigid frameworks, ASP.NET Core supports multiple deployment targets—ranging from cloud platforms like Azure and AWS to containerized environments with Docker and Kubernetes.
This adaptability ensures services can scale horizontally or vertically as application needs evolve.
Beneath the surface, the framework's modular design supports integration with various data access patterns. Whether using Entity Framework Core for database operations or external REST clients, developers maintain clean separation between business logic and infrastructure concerns. As noted in a developer community whitepaper: “ASP.NET Core Web API promotes loose coupling, making it easier to swap implementations without rewriting core application pathways.” This modularity enhances long-term maintainability and reduces technical debt.
Core Components That Power Web API Functionality
Building a functional Web API in ASP.NET Core relies on several foundational components that together ensure clean, efficient, and secure operations:
- Controllers: At the API layer, controllers determine how HTTP requests map to business actions.
Using model-views-controllers (MVC) patterns adapted for stateless services, they receive incoming requests, validate input via model binding, invoke corresponding logic, and return appropriate responses.
- Middleware Pipeline: Request processing flows through a configurable pipeline of middleware components. Critical middleware includes authentication (via JWT or OAuth), exception handling, logging, and CORS configuration. This structured flow allows developers to intercept and process requests uniformly.
- Model Binding and Validation
- Automated conversion of request data—JSON or form-encoded—into strongly-typed C# models.
- Data annotations like [Required], [Range], and [StringLength] enable automatic validation to ensure input integrity before processing.
- Data Transfer Objects (DTOs): Separating internal models from API responses via DTOs enhances security and flexibility.
DTOs expose only necessary properties, preventing over-exposure and enabling independent evolution of client and server contracts.
Security Meets Simplicity in ASP.NET Core APIs
Security is not an afterthought in ASP.NET Core Web API; it’s baked into the architecture. The framework integrates seamlessly with industry-standard authentication and authorization mechanisms, enabling developers to enforce robust access controls with minimal configuration.
For instance, JWT (JSON Web Tokens) authentication is supported out-of-the-box, allowing stateless verification of user identity across requests. Role-based and policy-based authorization further ensure that only authorized clients access protected endpoints.
James Whittaker, a senior .NET contributor, emphasizes: “ASP.NET Core’s built-in security features empower developers to enforce robust access policies without sacrificing performance or complicating the API surface.”
Additionally, the framework supports CORS—Cross-Origin Resource Sharing—enabling safe interactions across domains while preventing unauthorized cross-site requests. Authorization policies can be fine-tuned to restrict access by origin, role, or scope, making integration with modern, distributed frontends secure by design.
Error Handling and Logging Built for Reliability
Unreliable or uncommunicative APIs frustrate developers and degrade user experience. ASP.NET Core Web API addresses this through structured error handling that returns consistent, machine-readable error responses.
Unlike bare-metal implementations, the framework supports standardized error formats—including HTTP status codes, error messages, and contextual details—improving debugging and client-side handling.
Advanced logging integration, powered by Microsoft.Extensions.Logging, ensures every request and exception is recorded with granular metadata. Built-in diagnostics middleware collects performance metrics and traces, enabling proactive monitoring and rapid troubleshooting. Together, these tools transform error management from reactive chasing into proactive system insights.
Real-World Use Cases and Developer Efficiency
Adopting Web API in ASP.NET Core delivers tangible benefits across industries.
Consider a common scenario: building a food delivery application. A Web API serves as the backbone, powering a mobile app that retrieves real-time menu data, places orders, and provides live delivery tracking. With ASP.NET Core, developers quickly scaffold APIs for each endpoint—user authentication, menu management, order placement, payment processing—leveraging the framework’s rapid tooling and rich library support.
Another compelling use case involves hybrid architectures, where ASP.NET Core Web APIs act as a bridge between legacy backends and modern frontend frameworks like React or Blazor.
By exposing well-documented, versioned endpoints, teams maintain backward compatibility while enabling progressive enhancements to the client layer. This gradual modernization approach reduces risk and accelerates time-to-market.
The framework’s embedded OpenAPI/Swagger support further boosts developer efficiency. Auto-generated API documentation displays endpoints, request/response models, and security schemes—lessening the burden of manual docs and empowering frontend teams to integrate faster with confidence.
Best Practices for Developing Robust Web APIs
Despite its streamlined design, building reliable Web APIs demands discipline.
Key best practices include:
- Apply Versioning—Use URL versioning (e.g., /api/v1/orders) to maintain compatibility during updates.
- Embrace Rate Limiting—Prevent abuse with API keys, quotas, or token buckets enforced via middleware.
- Implement Caching—Use HTTP caching headers or distributed caches to reduce server load on frequent requests.
- Test Rigorously—Leverage tools like Postman or xUnit for automated unit, integration, and contract testing.
- Document Thoroughly—Keep OpenAPI specs up-to-date and accessible via Swagger UI.
- Secure Endpoints —Enforce authentication, validate inputs, and scope permissions precisely to minimize attack surface.
These practices collectively build APIs that are not only functional but resilient, secure, and developer-friendly.
ASP.NET Core’s design philosophy centers on simplicity without sacrificing power. Web APIs delivered through this framework exemplify that balance—delivering rapid development cycles, enterprise-grade reliability, and intuitive extensibility. As one enterprise architect noted, “With ASP.NET Core Web API, building scalable backends is no longer a heavy lift but a clear, strategic advantage.”
For modern software teams, mastering Web API in ASP.NET Core is not just about knowing a tool—it’s about embracing a scalable, secure, and future-ready approach to building the digital infrastructure that powers tomorrow’s applications.
Whether powering mobile experiences, cloud-native services, or cross-platform integrations, Web API in ASP.NET Core stands as a cornerstone of efficient and robust backend development—proven, performant, and primed for evolving needs.


Related Post

Burger King’s “Hot Off The Broiler”: Decoding the Sizzling New Menu Tagline

