Unlocking the City: Your Guide to Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks
Unlocking the City: Your Guide to Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks
In an era where urban density continues to rise and digital connectivity is no longer optional, cities are turning to Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks (WMANs) as the backbone of modern smart infrastructure. These dynamic wireless systems enable seamless communication across entire urban landscapes—supporting public safety, transportation, utilities, and citizen services with unprecedented speed and reliability. As metropolitan regions grapple with expansion and real-time data demands, understanding WMANs becomes essential for urban planners, technologists, and community leaders alike.
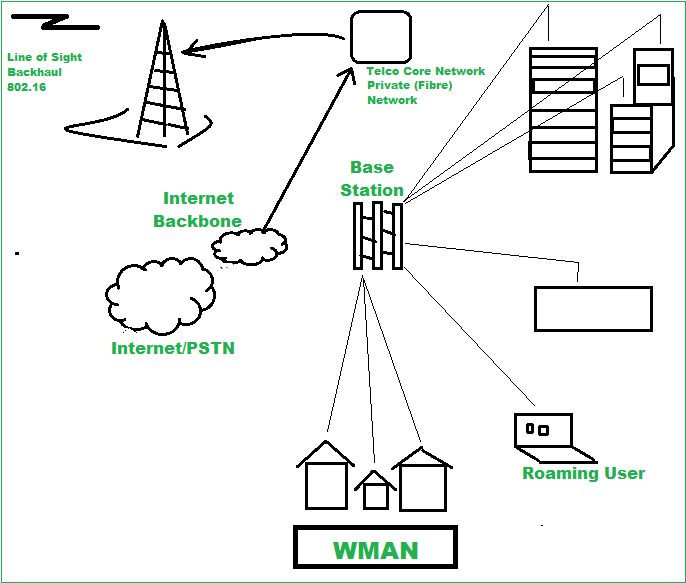
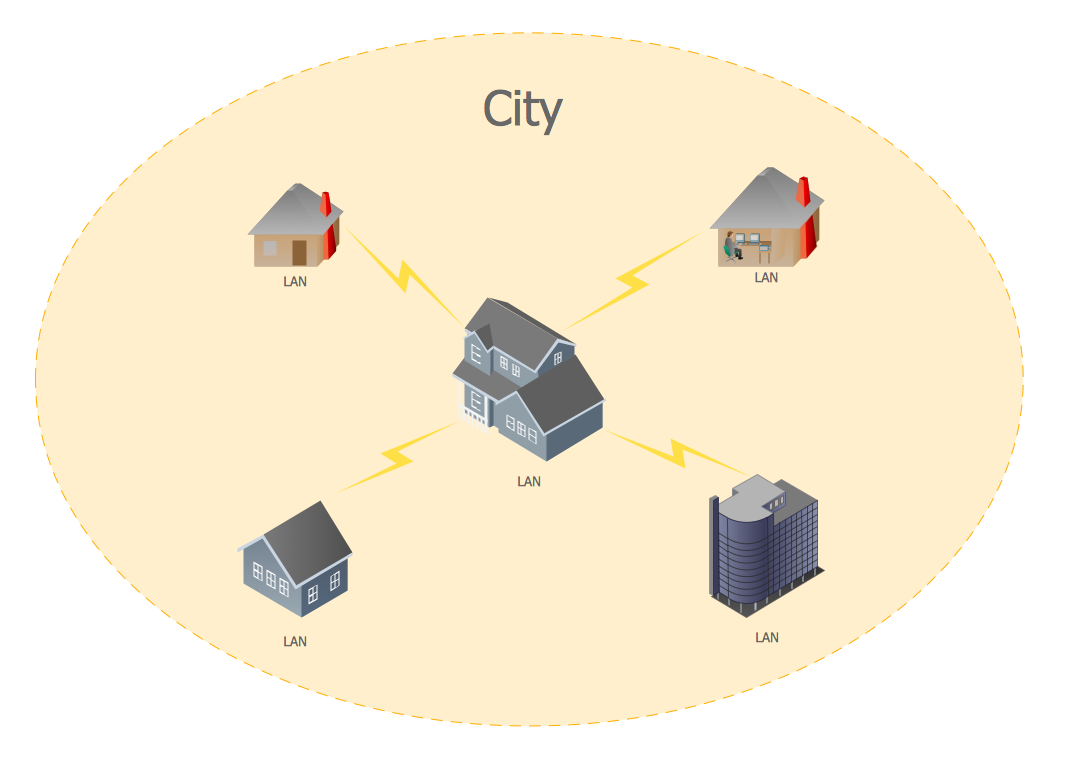
At its core, a Wireless Metropolitan Area Network connects key nodes across a city—government centers, transit hubs, hospitals, emergency stations, and public Wi-Fi hotspots—via high-performance wireless links. Unlike traditional wireless solutions confined to homes or offices, WMANs span hundreds of kilometers, delivering robust, scalable, and secure connectivity. “WMANs are transforming cities from collections of buildings into intelligent, responsive ecosystems,” notes Dr.
Elena Torres, a telecommunications engineer specializing in urban ICT infrastructure. “They enable cities to collect, analyze, and act on data in real time, fundamentally changing how urban services operate.”
The Building Blocks of Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks
WMANs rely on a combination of advanced wireless technologies optimized for urban scale. The most prominent include: - Wi-Fi-based networks: High-capacity Wi-Fi 6 and 6E systems provide last-mile connectivity, ideal for dense public areas.- Fixed wireless access (FWA): Using directional antennas and beamforming, FWA delivers high-speed broadband without physical cabling, ideal for underserved neighborhoods. - Private LTE and 5G networks: These mobile technologies offer ultra-low latency and high throughput, essential for mission-critical systems like traffic management and smart grids. - Mesh networking: Distributed nodes maintain resilience by rerouting data, ensuring continuous operation even if part of the network fails.
Each layer serves a strategic purpose, working in concert to support seamless urban operations. “The flexibility of modern WMANs means cities can deploy solutions tailored to specific needs—be it emergency response, environmental monitoring, or digital equity initiatives,” says Marcus Chen, Director of Urban Connectivity at MetroNet Solutions.
Network topology plays a crucial role in scalability and performance.
Most WMANs adopt a hybrid architecture combining centralized core data centers with decentralized access points. This model enables efficient load balancing, reduces latency, and enhances fault tolerance. For example, edge computing nodes placed throughout the city process data locally, minimizing transmission bottlenecks while preserving privacy and security.
\begin{itemize} \item Performance metrics: Latency typically under 50 milliseconds; upload and download speeds exceed 1 Gbps in dense zones. \item Security protocols: End-to-end encryption, strict access controls, and continuous monitoring protect citizens’ data. \item Scalability: WMANs can expand quickly via modular add-ons, adapting to growing populations and emerging technologies.
\end{itemize> In intelligent transportation systems, WMANs power real-time traffic signal coordination, enabling adaptive traffic flow and reducing congestion by up to 30%, according to city pilot programs in Barcelona and Singapore. Emergency services leverage these networks to dispatch resources faster and maintain communication during disasters, reinforcing public safety. Public Wi-Fi hotspots not only close the digital divide but also enhance urban livability and support tourism and local economies.
Implementing a WMAN requires careful planning and stakeholder collaboration. Key considerations include: - Regulatory compliance with spectrum allocation and licensing. - Branding and governance models to manage public access ethically.
- Interoperability standards that allow integration with existing municipal IT systems. - Community engagement to build trust and ensure equitable deployment. Cities like Tokyo and Copenhagen have demonstrated success through phased rollouts, beginning with high-impact corridors before expanding citywide.
These pilots underscore the importance of evidence-based planning supported by data analytics and continuous monitoring. Emerging technologies are further amplifying WMAN potential. Artificial intelligence enhances network optimization by predicting usage patterns and dynamically adjusting bandwidth.
Satellite backhaul strengthens connectivity in remote or underserved urban zones. Moreover, open-access network models empower local operators and startups to innovate, fostering competitive, citizen-centric services. \begin quo>“Wireless metropolitan networks are not just infrastructure—they’re enablers of sustainable, inclusive, and responsive cities,” asserts Dr.
Rajiv Patel, Chief Technology Officer at UrbanConnect. “As urban life evolves, so must our connectivity. WMANs lay the groundwork for cities that think, learn, and react in real time.” Beyond supporting core services, WMANs catalyze smart city innovation by enabling data-driven decision-making.
Sensors embedded in streetlights, waste bins, and transit vehicles feed vast streams of information—measured in terabytes daily—into centralized platforms. Analytics engines interpret this data to optimize energy use, improve waste collection routes, and forecast public health trends. In summary, Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks represent a transformative leap in urban infrastructure.
By unifying communication across functions and sectors, they empower cities to operate efficiently, respond swiftly, and enhance quality of life. As digital transformation accelerates, WMANs stand at the forefront of building resilient, intelligent, and inclusive metropolitan futures. Unlocking the City: Your Guide to Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks shows how these networks are not merely technical solutions but foundational pillars of the modern, connected metropolis—reshaping daily life one wireless link at a time.

Related Post

HDMovie2: Your Ultimate Guide to Streaming Movies Online — No Ads, No Limits
Beyond the Prosthetics: The Impressive Journey of Sage Gold Marshall
Brian Craig Show Bio Wiki Age Wife Salary and Net Worth

Barry B Benson Voices the Star of ‘Bee Movie’: The Bee Who Changed Animation History

